Randomized controlled trial of a mailed toolkit to increase use of body mass index percentiles to screen for childhood obesity
- PMID: 19754998
- PMCID: PMC2774636
Randomized controlled trial of a mailed toolkit to increase use of body mass index percentiles to screen for childhood obesity
Abstract
Introduction: Despite epidemic increases in childhood obesity rates, many providers fail to diagnose obesity. Body mass index (BMI)-for-age percentiles are the recommended screening test. We evaluated whether mailing a toolkit to physicians would increase use of sex-specific BMI-for-age percentiles to screen for childhood obesity.
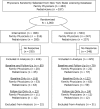
Methods: We assigned a random sample of family physicians and pediatricians from New York State's medical licensing database to either intervention or control groups in the summer of 2004. At baseline and at follow-up, we sent physicians a survey that asked how often they used various screening methods to identify childhood obesity. Between the surveys, we sent physicians in the intervention group a toolkit that consisted of professional guidelines for childhood obesity screening, a tool for calculating BMI, BMI-for-age growth charts, and educational information.
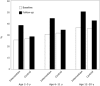
Results: At follow-up, more physicians in the intervention group than in the control group reported using BMI percentiles to screen for childhood obesity. Compared with physicians in the control group, physicians in the intervention group had a larger increase in their routine use of BMI percentiles to screen children aged 2 to 5, 6 to 11, and 12 to 20 years, although the differences in the older 2 groups did not attain statistical significance.
Conclusion: Directly mailing an educational toolkit to physicians can have a small but positive effect on clinical practice.
Figures
References
-
- The Surgeon General's call to action to prevent and decrease overweight and obesity, 2001. Rockville (MD): US Department of Health and Human Services, Office of the Surgeon General; 2001. [Accessed June 1, 2009]. http://www.surgeongeneral.gov/topics/obesity/ calltoaction/CalltoAction.pdf . - PubMed
-
- Barlow SE, Dietz WH. Obesity evaluation and treatment: expert committee recommendations. Pediatrics. 1998;102(3):E29. - PubMed
-
- Mei Z, Grummer-Strawn LM, Pietrobelli A, Goulding A, Goran MI, Dietz WH. Validity of body mass index compared with other body-composition screening indexes for the assessment of body fatness in children and adolescents. Am J Clin Nutr. 2002;75(6):978–985. - PubMed
-
- Pietrobelli A, Faith MS, Allison DB, Gallagher D, Chiumello G, Heymsfield SB. Body mass index as a measure of adiposity among children and adolescents: a validation study. J Pediatr. 1998;132(2):204–210. - PubMed
-
- Freedman DS, Khan LK, Serdula MK, Dietz WH, Srinivasan SR, Berenson GS. The relation of childhood BMI to adult adiposity: the Bogalusa Heart Study. Pediatrics. 2005;115(1):22–27. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

