Radial extracorporeal shockwave treatment compared with supervised exercises in patients with subacromial pain syndrome: single blind randomised study
- PMID: 19755551
- PMCID: PMC2744862
- DOI: 10.1136/bmj.b3360
Radial extracorporeal shockwave treatment compared with supervised exercises in patients with subacromial pain syndrome: single blind randomised study
Abstract
Objective: To compare the effectiveness of radial extracorporeal shockwave treatment with that of supervised exercises in patients with shoulder pain.
Design: Single blind randomised study.
Setting: Outpatient clinic of physical medicine and rehabilitation department in Oslo, Norway.
Participants: 104 patients with subacromial shoulder pain lasting at least three months.
Interventions: Radial extracorporeal shockwave treatment: one session weekly for four to six weeks. Supervised exercises: two 45 minute sessions weekly for up to 12 weeks. Primary outcome measure Shoulder pain and disability index.
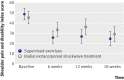
Results: A treatment effect in favour of supervised exercises at 6, 12, and 18 weeks was found. The adjusted treatment effect was -8.4 (95% confidence interval -16.5 to -0.6) points. A significantly higher proportion of patients in the group treated with supervised exercises improved-odds ratio 3.2 (1.3 to 7.8). More patients in the shockwave treatment group had additional treatment between 12 and 18 weeks-odds ratio 5.5 (1.3 to 26.4).
Conclusion: Supervised exercises were more effective than radial extracorporeal shockwave treatment for short term improvement in patients with subacromial shoulder pain.
Trial registration: Clinical trials NCT00653081.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
Comment in
-
Radial extracorporeal shockwave treatment or supervised exercises for subacromial pain syndrome?Clin J Sport Med. 2010 May;20(3):225. doi: 10.1097/01.jsm.0000373159.82858.ad. Clin J Sport Med. 2010. PMID: 20445371 No abstract available.
-
Supervised exercises are more effective for subacromial pain than extracorporeal shockwave treatment.J Physiother. 2010;56(1):58. doi: 10.1016/s1836-9553(10)70056-4. J Physiother. 2010. PMID: 20500139 No abstract available.
References
-
- Faber E, Kuiper JI, Burdorf A, Miedema HS, Verhaar JA. Treatment of impingement syndrome: a systematic review of the effects on functional limitations and return to work. J Occup Rehabil 2006;16:7-25. - PubMed
-
- Brox JI. Shoulder pain. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol 2003;17:33-56. - PubMed
-
- Blaine TA, Kim YS, Voloshin I, Chen D, Murakami K, Chang SS, et al. The molecular pathophysiology of subacromial bursitis in rotator cuff disease. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 2005;14(1 suppl S):84-9S. - PubMed
-
- Bohmer A, Staff PH, Brox JI. Supervised exercises in relation to rotator cuff disease (impingement syndrome, stages 1 and II): a treatment regimen and its rationale. Physiother Theory Pract 1998;14:93-105.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical