Erythropoietin modulates the neural control of hypoxic ventilation
- PMID: 19756385
- PMCID: PMC11115915
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-009-0142-z
Erythropoietin modulates the neural control of hypoxic ventilation
Abstract
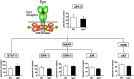
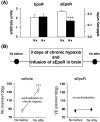
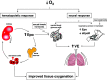
Numerous factors involved in general homeostasis are able to modulate ventilation. Classically, this comprises several kind of molecules, including neurotransmitters and steroids that are necessary for fine tuning ventilation under different conditions such as sleep, exercise, and acclimatization to high altitude. Recently, however, we have found that erythropoietin (Epo), the main regulator of red blood cell production, influences both central (brainstem) and peripheral (carotid bodies) respiratory centers when the organism is exposed to hypoxic conditions. Here, we summarize the effect of Epo on the respiratory control in mammals and highlight the potential implication of Epo in the ventilatory acclimatization to high altitude, as well as in the several respiratory sickness and syndromes occurring at low and high altitude.
Figures
References
-
- Fisher JW. Erythropoietin: physiologic, pharmacologic aspects. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1997;216:358–369. - PubMed
-
- Jelkmann W. Erythropoietin: structure, control of production, function. Physiol Rev. 1992;72:449–489. - PubMed
-
- Sasaki R, Masuda S, Nagao M. Pleiotropic functions and tissue-specific expression of erythropoietin. News Physiol Sci. 2001;16:110–113. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

