Computer-aided quantification of retinal neovascularization
- PMID: 19757106
- PMCID: PMC4005267
- DOI: 10.1007/s10456-009-9155-3
Computer-aided quantification of retinal neovascularization
Abstract
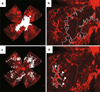
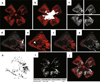
Rodent models of retinal angiogenesis play a pivotal role in angiogenesis research. These models are a window to developmental angiogenesis, to pathological retinopathy, and are also in vivo tools for anti-angiogenic drug screening in cancer and ophthalmic research. The mouse model of oxygen-induced retinopathy (OIR) has emerged as one of the leading in vivo models for these purposes. Many of the animal studies that laid the foundation for the recent breakthrough of anti-angiogenic treatments into clinical practice were performed in the OIR model. However, readouts from the OIR model have been time-consuming and can vary depending on user experience. Here, we present a computer-aided quantification method that is characterized by (i) significantly improved efficiency, (ii) high correlation with the established hand-measurement protocols, and (iii) high intra- and inter-individual reproducibility of results. This method greatly facilitates quantification of retinal angiogenesis while at the same time increasing lab-to-lab reproducibility of one of the most widely used in vivo models in angiogenesis research.
Figures

References
-
- Kennedy D. Breakthrough of the Year. Science. 2006:1841. - PubMed
-
- Rosenfeld PJ, et al. Ranibizumab for neovascular age-related macular degeneration. N Engl J Med. 2006;355(14):1419–1431. - PubMed
-
- Ranieri G, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) as a target of bevacizumab in cancer: from the biology to the clinic. Curr Med Chem. 2006;13(16):1845–1857. - PubMed
-
- Smith LE, et al. Oxygen-induced retinopathy in the mouse. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1994;35(1):101–111. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

