Mycobacterium tuberculosis strains with highly discordant rifampin susceptibility test results
- PMID: 19759221
- PMCID: PMC2772627
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.01209-09
Mycobacterium tuberculosis strains with highly discordant rifampin susceptibility test results
Abstract
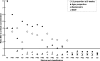
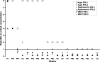
The objectives of this study were to investigate the origin of highly discordant rifampin (rifampicin) (RMP) drug susceptibility test results obtained for Mycobacterium tuberculosis strains during proficiency testing. Nine Supra-National Tuberculosis Reference Laboratories tested the RMP susceptibilities of 19 selected M. tuberculosis strains, using standard culture-based methods. The strains were classified as definitely resistant (R) (n = 6) or susceptible (S) (n = 2) or probably resistant (PR) (n = 8) or susceptible (PS) (n = 3) based on rpoB mutations and treatment outcome. All methods yielded a susceptible result for the two S and three PS strains lacking an rpoB mutation and a resistant result for one R strain with a Ser531Leu mutation and one PR strain with a double mutation. Although the remaining 12 R and PR strains had rpoB mutations (four Asp516Tyr, three Leu511Pro, two Leu533Pro, one each His526Leu/Ser, and one Ile572Phe), they were all susceptible by the radiometric Bactec 460TB or Bactec 960 MGIT methods. In contrast, only one was susceptible by the proportion method on Löwenstein-Jensen medium and two on Middlebrook 7H10 agar. Low-level but probably clinically relevant RMP resistance linked to specific rpoB mutations is easily missed by standard growth-based methods, particularly the automated broth-based systems. Further studies are required to confirm these findings, to determine the frequency of these low-level-resistant isolates, and to identify technical improvements that may identify such strains.
Figures

References
-
- Barnard, M., H. Albert, G. Coetzee, R. O'Brien, and M. E. Bosman. 2008. Rapid molecular screening for multidrug-resistant tuberculosis in a high-volume public health laboratory in South Africa. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 177:787-792. - PubMed
-
- Espinal, M. A., S. J. Kim, P. G. Suarez, K. M. Kam, A. G. Khomenko, G. B. Migliori, J. Baéz, A. Kochi, C. Dye, and M. C. Raviglione. 2000. Standard short-course chemotherapy for drug-resistant tuberculosis. Treatment outcomes in 6 countries. JAMA 283:2537-2545. - PubMed
-
- Gagneux, S., C. Davis Long, P. M. Small, T. Van, G. K. Schoolnik, and B. J. M. Bohannan. 2006. The competitive cost of antibiotic resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Science 312:1944-1946. - PubMed
-
- Gillespie, S. H., O. J. Billington, A. Breathnach, and T. D. McHugh. 2002. Multiple drug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis: evidence for changing fitness following passage through human hosts. Microb. Drug Resist. 8:273-279. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

