Non-spa-typeable clinical Staphylococcus aureus strains are naturally occurring protein A mutants
- PMID: 19759222
- PMCID: PMC2772612
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.00941-09
Non-spa-typeable clinical Staphylococcus aureus strains are naturally occurring protein A mutants
Abstract
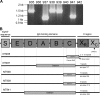
Staphylococcus aureus is a major human pathogen responsible for increasing the prevalence of community- and hospital-acquired infections. Protein A (SpA) is a key virulence factor of S. aureus and is highly conserved. Sequencing of the variable-number tandem-repeat region of SpA (spa typing) provides a rapid and reliable method for epidemiological studies. Rarely, non-spa-typeable S. aureus strains are encountered. The reason for this is not known. In this study, we characterized eight non-spa-typeable bacteremia isolates. Sequencing of the entire spa locus was successful for five strains and revealed various mutations of spa, all of which included a deletion of immunoglobulin G binding domain C, in which the upper primer for spa typing is located, while two strains were truly spa negative. This is the first report demonstrating that nontypeability of S. aureus by spa sequencing is due either to mutation or to a true deficiency of spa.
Figures


References
-
- Aires-de-Sousa, M., K. Boye, H. de Lencastre, A. Deplano, M. C. Enright, J. Etienne, A. Friedrich, D. Harmsen, A. Holmes, X. W. Huijsdens, A. M. Kearns, A. Mellmann, H. Meugnier, J. K. Rasheed, E. Spalburg, B. Strommenger, M. J. Struelens, F. C. Tenover, J. Thomas, U. Vogel, H. Westh, J. Xu, and W. Witte. 2006. High interlaboratory reproducibility of DNA sequence-based typing of bacteria in a multicenter study. J. Clin. Microbiol. 44:619-621. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Boucher, H. W., and G. R. Corey. 2008. Epidemiology of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Clin. Infect. Dis. 46(Suppl. 5):S344-S349. - PubMed
-
- Chatterjee, I., M. Herrmann, R. A. Proctor, G. Peters, and B. C. Kahl. 2007. Enhanced post-stationary-phase survival of a clinical thymidine-dependent small-colony variant of Staphylococcus aureus results from lack of a functional tricarboxylic acid cycle. J. Bacteriol. 189:2936-2940. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cosgrove, S. E., G. Sakoulas, E. N. Perencevich, M. J. Schwaber, A. W. Karchmer, and Y. Carmeli. 2003. Comparison of mortality associated with methicillin-resistant and methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia: a meta-analysis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 36:53-59. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

