A novel liposome-based adjuvant CAF01 for induction of CD8(+) cytotoxic T-lymphocytes (CTL) to HIV-1 minimal CTL peptides in HLA-A*0201 transgenic mice
- PMID: 19759892
- PMCID: PMC2736401
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0006950
A novel liposome-based adjuvant CAF01 for induction of CD8(+) cytotoxic T-lymphocytes (CTL) to HIV-1 minimal CTL peptides in HLA-A*0201 transgenic mice
Abstract
Background: Specific cellular cytotoxic immune responses (CTL) are important in combating viral diseases and a highly desirable feature in the development of targeted HIV vaccines. Adjuvants are key components in vaccines and may assist the HIV immunogens in inducing the desired CTL responses. In search for appropriate adjuvants for CD8(+) T cells it is important to measure the necessary immunological features e.g. functional cell killing/lysis in addition to immunological markers that can be monitored by simple immunological laboratory methods.
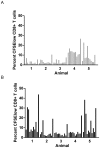
Methodology/principal findings: We tested the ability of a novel two component adjuvant, CAF01, consisting of the immune stimulating synthetic glycolipid TDB (Trehalose-Dibehenate) incorporated into cationic DDA (Dimethyldioctadecylammonium bromide) liposomes to induce CD8(+) T-cell restricted cellular immune responses towards subdominant minimal HLA-A0201-restricted CTL epitopes from HIV-1 proteins in HLA-A*0201 transgenic HHD mice. CAF01 has an acceptable safety profile and is used in preclinical development of vaccines against HIV-1, malaria and tuberculosis.
Conclusions/significance: We found that CAF01 induced cellular immune responses against HIV-1 minimal CTL epitopes in HLA-A*0201 transgenic mice to levels comparable with that of incomplete Freund's adjuvant.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
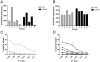
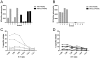
References
-
- Vangala A, Kirby D, Rosenkrands I, Agger EM, Andersen P, et al. A comparative study of cationic liposome and niosome-based adjuvant systems for protein subunit vaccines: characterisation, environmental scanning electron microscopy and immunisation studies in mice. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2006;58:787–799. - PubMed
-
- Davidsen J, Rosenkrands I, Christensen D, Vangala A, Kirby D, et al. Characterization of cationic liposomes based on dimethyldioctadecylammonium and synthetic cord factor from M. tuberculosis (trehalose 6,6′-dibehenate)-a novel adjuvant inducing both strong CMI and antibody responses. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2005;1718:22–31. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

