A survey of integral alpha-helical membrane proteins
- PMID: 19760129
- PMCID: PMC2780624
- DOI: 10.1007/s10969-009-9069-8
A survey of integral alpha-helical membrane proteins
Abstract
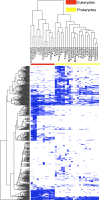
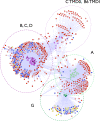
Membrane proteins serve as cellular gatekeepers, regulators, and sensors. Prior studies have explored the functional breadth and evolution of proteins and families of particular interest, such as the diversity of transport-associated membrane protein families in prokaryotes and eukaryotes, the composition of integral membrane proteins, and family classification of all human G-protein coupled receptors. However, a comprehensive analysis of the content and evolutionary associations between membrane proteins and families in a diverse set of genomes is lacking. Here, a membrane protein annotation pipeline was developed to define the integral membrane genome and associations between 21,379 proteins from 34 genomes; most, but not all of these proteins belong to 598 defined families. The pipeline was used to provide target input for a structural genomics project that successfully cloned, expressed, and purified 61 of our first 96 selected targets in yeast. Furthermore, the methodology was applied (1) to explore the evolutionary history of the substrate-binding transmembrane domains of the human ABC transporter superfamily, (2) to identify the multidrug resistance-associated membrane proteins in whole genomes, and (3) to identify putative new membrane protein families.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The evolutionary repertoires of the eukaryotic-type ABC transporters in terms of the phylogeny of ATP-binding domains in eukaryotes and prokaryotes.Mol Biol Evol. 2004 Nov;21(11):2149-60. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msh226. Epub 2004 Aug 5. Mol Biol Evol. 2004. PMID: 15297601
-
The ABC transporter gene family of Caenorhabditis elegans has implications for the evolutionary dynamics of multidrug resistance in eukaryotes.Genome Biol. 2004;5(3):R15. doi: 10.1186/gb-2004-5-3-r15. Epub 2004 Feb 11. Genome Biol. 2004. PMID: 15003118 Free PMC article.
-
Topological analysis of integral membrane constituents of prokaryotic ABC efflux systems.Res Microbiol. 2005 Mar;156(2):270-7. doi: 10.1016/j.resmic.2004.07.010. Epub 2004 Nov 11. Res Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 15748994
-
Plant ABC transporters.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000 May 1;1465(1-2):79-103. doi: 10.1016/s0005-2736(00)00132-2. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000. PMID: 10748248 Review.
-
Multidrug resistance: molecular mechanisms and clinical relevance.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1997;40 Suppl:S3-8. doi: 10.1007/s002800051053. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1997. PMID: 9272126 Review.
Cited by
-
Structural analysis of a peptide fragment of transmembrane transporter protein bilitranslocase.PLoS One. 2012;7(6):e38967. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0038967. Epub 2012 Jun 20. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22745694 Free PMC article.
-
FUN26 (function unknown now 26) protein from saccharomyces cerevisiae is a broad selectivity, high affinity, nucleoside and nucleobase transporter.J Biol Chem. 2014 Aug 29;289(35):24440-51. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.553503. Epub 2014 Jul 17. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 25035431 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of human solute carriers.Protein Sci. 2010 Mar;19(3):412-28. doi: 10.1002/pro.320. Protein Sci. 2010. PMID: 20052679 Free PMC article.
-
Coordinating the impact of structural genomics on the human α-helical transmembrane proteome.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2013 Feb;20(2):135-8. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2508. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23381628 Free PMC article.
-
Structure-based discovery of prescription drugs that interact with the norepinephrine transporter, NET.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Sep 20;108(38):15810-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1106030108. Epub 2011 Sep 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21885739 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

