Activation of membrane NADPH oxidase associated with lysosome-targeted acid sphingomyelinase in coronary endothelial cells
- PMID: 19761405
- PMCID: PMC2834561
- DOI: 10.1089/ars.2009.2461
Activation of membrane NADPH oxidase associated with lysosome-targeted acid sphingomyelinase in coronary endothelial cells
Abstract
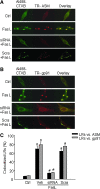
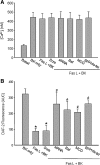
This study explored the mechanism mediating the aggregation of membrane NADPH oxidase (NOX) subunits and subsequent activation of this enzyme in bovine coronary arterial endothelial cells (CAECs). With confocal microscopy, we found that FasL stimulated lipid rafts (LRs) clustering with NOX subunit aggregation and acid sphingomyelinase (ASM) gathering, which was blocked by the siRNA of sortilin, an intracellular protein responsible for the binding and targeting of ASM to lysosomes. Correspondingly, FasL-induced O(2)(.-) production through NOX in LRs fractions was abolished by sortilin siRNA. Further, with flow-cytometry and fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) analysis, we surprisingly demonstrated that after FasL stimulation, sortilin was exposed to cell membranes from lysosomes together with Lamp-1 and ASM, and these lysosomal components were aggregated and form a signaling complex in cell membranes. With co-immunoprecipitation, lysosomal sortilin and ASM were found to interact more strongly when CAECs were stimulated by FasL. Functionally, inhibition of either sortilin expression, lysosome function, LRs clustering, or NOX activity significantly attenuated FasL-induced decrease in nitric oxide (NO) levels. It is concluded that lysosome-targeted ASM, through sortilin, is able to traffic to and expose to cell-membrane surface, which may lead to LRs clustering and NOX activation in CAECs.
Figures



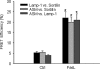

References
-
- Babior BM. NADPH oxidase. Curr Opin Immunol. 2004;16:42–47. - PubMed
-
- Baranski TJ. Faust PL. Kornfeld S. Generation of a lysosomal enzyme targeting signal in the secretory protein pepsinogen. Cell. 1990;63:281–291. - PubMed
-
- Barrachina M. Maes T. Buesa C. Ferrer I. Lysosome-associated membrane protein 1 (LAMP-1) in Alzheimer's disease. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2006;32:505–516. - PubMed
-
- Canuel M. Lefrancois S. Zeng J. Morales CR. AP-1 and retromer play opposite roles in the trafficking of sortilin between the Golgi apparatus and the lysosomes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008;366:724–730. - PubMed
-
- Fauchais AL. Lalloue F. Lise MC. Boumediene A. Prud'homme JL. Vidal E. Jauberteau MO. Role of endogenous brain-derived neurotrophic factor and sortilin in B cell survival. J Immunol. 2008;181:3027–3038. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

