Phase Coupled Meta-analysis: sensitive detection of oscillations in cell cycle gene expression, as applied to fission yeast
- PMID: 19761608
- PMCID: PMC2753555
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-10-440
Phase Coupled Meta-analysis: sensitive detection of oscillations in cell cycle gene expression, as applied to fission yeast
Abstract
Background: Many genes oscillate in their level of expression through the cell division cycle. Previous studies have identified such genes by applying Fourier analysis to cell cycle time course experiments. Typically, such analyses generate p-values; i.e., an oscillating gene has a small p-value, and the observed oscillation is unlikely due to chance. When multiple time course experiments are integrated, p-values from the individual experiments are combined using classical meta-analysis techniques. However, this approach sacrifices information inherent in the individual experiments, because the hypothesis that a gene is regulated according to the time in the cell cycle makes two independent predictions: first, that an oscillation in expression will be observed; and second, that gene expression will always peak in the same phase of the cell cycle, such as S-phase. Approaches that simply combine p-values ignore the second prediction.
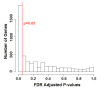
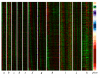
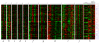
Results: Here, we improve the detection of cell cycle oscillating genes by systematically taking into account the phase of peak gene expression. We design a novel meta-analysis measure based on vector addition: when a gene peaks or troughs in all experiments in the same phase of the cell cycle, the representative vectors add to produce a large final vector. Conversely, when the peaks in different experiments are in various phases of the cycle, vector addition produces a small final vector. We apply the measure to ten genome-wide cell cycle time course experiments from the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe, and detect many new, weakly oscillating genes.
Conclusion: A very large fraction of all genes in S. pombe, perhaps one-quarter to one-half, show some cell cycle oscillation, although in many cases these oscillations may be incidental rather than adaptive.
Figures

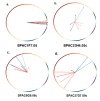
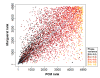
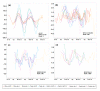
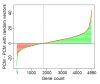
Similar articles
-
The cell cycle-regulated genes of Schizosaccharomyces pombe.PLoS Biol. 2005 Jul;3(7):e225. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0030225. Epub 2005 Jun 28. PLoS Biol. 2005. PMID: 15966770 Free PMC article.
-
A genome-wide resource of cell cycle and cell shape genes of fission yeast.Open Biol. 2013 May 22;3(5):130053. doi: 10.1098/rsob.130053. Open Biol. 2013. PMID: 23697806 Free PMC article.
-
The more the merrier: comparative analysis of microarray studies on cell cycle-regulated genes in fission yeast.Yeast. 2006 Mar;23(4):261-277. doi: 10.1002/yea.1351. Yeast. 2006. PMID: 16544289 Free PMC article.
-
Cell cycle regulated gene expression in yeasts.Adv Genet. 2011;73:51-85. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-380860-8.00002-1. Adv Genet. 2011. PMID: 21310294 Review.
-
Controlling cell cycle progress in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1991 Oct;1(3):307-12. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(05)80292-8. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1991. PMID: 1840886 Review.
Cited by
-
Comprehensive literature review and statistical considerations for microarray meta-analysis.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 May;40(9):3785-99. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr1265. Epub 2012 Jan 19. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22262733 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A new transcription factor for mitosis: in Schizosaccharomyces pombe, the RFX transcription factor Sak1 works with forkhead factors to regulate mitotic expression.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Aug 18;43(14):6874-88. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv274. Epub 2015 Apr 23. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 25908789 Free PMC article.
-
Dissecting the fission yeast regulatory network reveals phase-specific control elements of its cell cycle.BMC Syst Biol. 2009 Sep 16;3:93. doi: 10.1186/1752-0509-3-93. BMC Syst Biol. 2009. PMID: 19758441 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Laub MT, McAdams HH, Feldblyum T, Fraser CM, Shapiro L. Global analysis of the genetic network controlling a bacterial cell cycle. Science (New York, NY) 2000;290:2144–2148. - PubMed
-
- Whitfield ML, Sherlock G, Saldanha AJ, Murray JI, Ball CA, Alexander KE, Matese JC, Perou CM, Hurt MM, Brown PO, et al. Identification of genes periodically expressed in the human cell cycle and their expression in tumors. Molecular biology of the cell. 2002;13:1977–2000. doi: 10.1091/mbc.02-02-0030.. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

