Differential expression of Salmonella type III secretion system factors InvJ, PrgJ, SipC, SipD, SopA and SopB in cultures and in mice
- PMID: 19762438
- PMCID: PMC2889428
- DOI: 10.1099/mic.0.032318-0
Differential expression of Salmonella type III secretion system factors InvJ, PrgJ, SipC, SipD, SopA and SopB in cultures and in mice
Abstract
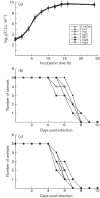
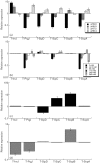
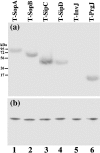
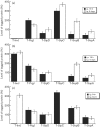
The type III secretion system (T3SS) encoded by Salmonella pathogenicity island 1 (SPI-1) is important for the invasion of epithelial cells during development of Salmonella-associated enterocolitis. It has been suggested that the level and timing of the expression of the SPI-1 T3SS proteins and effectors dictate the consequences of bacterial infection and pathogenesis. However, the expression of these proteins has not been extensively studied in vivo, especially during the later stages of salmonellosis when the infection is established. We have constructed recombinant Salmonella strains that contain a FLAG epitope inserted in-frame to genes invJ, prgJ, sipC, sipD, sopA and sopB, and investigated the expression of the tagged proteins both in vitro and in vivo during murine salmonellosis. Mice were inoculated intraperitoneally or intragastrically with the tagged Salmonella strains. At different time points post-infection, bacteria were recovered from various organs, and the expression of the tagged proteins was determined. Our results provide direct evidence that PrgJ and SipD are expressed in Salmonella colonizing the liver and ileum of infected animals at both the early and late stages of infection. Furthermore, our study has shown that the InvJ protein is expressed preferentially in Salmonella colonizing the ileum but not the liver, while SipC is expressed preferentially in Salmonella colonizing the liver but not the ileum. Thus, Salmonella appears to express different SPI-1 proteins and effectors when colonizing specific tissues. Our results suggest that differential expression of these proteins may be important for tissue-specific aspects of bacterial pathogenesis such as gastroenterititis in the ileum and systemic infection in the liver.
Figures

References
-
- Abrahams, G. L. & Hensel, M. (2006). Manipulating cellular transport and immune responses: dynamic interactions between intracellular Salmonella enterica and its host cells. Cell Microbiol 8, 728–737. - PubMed
-
- Arricau, N., Hermant, D., Waxin, H., Ecobichon, C., Duffey, P. S. & Popoff, M. Y. (1998). The RcsB-RcsC regulatory system of Salmonella typhi differentially modulates the expression of invasion proteins, flagellin and Vi antigen in response to osmolarity. Mol Microbiol 29, 835–850. - PubMed
-
- Bajaj, V., Lucas, R. L., Hwang, C. & Lee, C. A. (1996). Co-ordinate regulation of Salmonella typhimurium invasion genes by environmental and regulatory factors is mediated by control of hilA expression. Mol Microbiol 22, 703–714. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

