Method of glomerular filtration rate estimation affects prediction of mortality risk
- PMID: 19762497
- PMCID: PMC2754107
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2008090980
Method of glomerular filtration rate estimation affects prediction of mortality risk
Abstract
Decreased kidney function, determined using a serum creatinine-based estimation of GFR, is associated with a higher risk for mortality from cardiovascular disease. Equations incorporating cystatin C improve the estimation of GFR, but whether this improves the prediction of risk for mortality is unknown. We measured cystatin C on 6942 adult participants in the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey Linked Mortality File, including all participants who had high serum creatinine (>1.2 mg/dl for men; >1.0 mg/dl for women) or were older than 60 yr and 25% random sample of participants who were younger than 60 yr. We estimated GFR using equations that included standardized serum creatinine, cystatin C, or both. Participant data were linked to the National Death Index. A total of 1573 (22.7%) deaths (713 deaths from cardiovascular disease) occurred during a median of 8 yr. Lower estimated GFR based on cystatin C was strongly associated with higher risk for overall and cardiovascular mortality across the range of normal to moderately decreased estimated GFR. Creatinine-based estimates of GFR resulted in weaker associations, with the association between estimated GFR and all-cause mortality reversed at higher levels of estimated GFR. An equation using both creatinine and cystatin C (in addition to age, race, and gender) resulted in weaker associations than equations using only cystatin C (with or without age, race, and gender). In conclusion, despite better performance in terms of estimating GFR, equations based on both cystatin C and creatinine do not predict mortality as well as equations based on cystatin C alone.
Figures
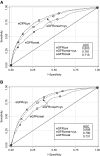
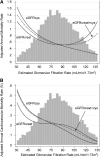
Comment in
-
More evidence that cystatin C predicts mortality better than creatinine.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009 Oct;20(10):2088-90. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2009080832. Epub 2009 Sep 17. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009. PMID: 19762490 No abstract available.
References
-
- Sarnak MJ, Levey AS, Schoolwerth AC, Coresh J, Culleton B, Hamm LL, McCullough PA, Kasiske BL, Kelepouris E, Klag MJ, Parfrey P, Pfeffer M, Raij L, Spinosa DJ, Wilson PW: Kidney disease as a risk factor for development of cardiovascular disease: A statement from the American Heart Association Councils on Kidney in Cardiovascular Disease, High Blood Pressure Research, Clinical Cardiology, and Epidemiology and Prevention. Circulation 108: 2154–2169, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Coresh J, Astor BC, Sarnak MJ: Evidence for increased cardiovascular disease risk in patients with chronic kidney disease. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 13: 73–81, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Go AS, Chertow GM, Fan D, McCulloch CE, Hsu CY: Chronic kidney disease and the risks of death, cardiovascular events, and hospitalization. N Engl J Med 351: 1296–1305, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Stevens LA, Coresh J, Greene T, Levey AS: Assessing kidney function: Measured and estimated glomerular filtration rate. N Engl J Med 354: 2473–2483, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Coresh J, Astor BC, McQuillan G, Kusek J, Greene T, Van Lente F, Levey AS: Calibration and random variation of the serum creatinine assay as critical elements of using equations to estimate glomerular filtration rate. Am J Kidney Dis 39: 920–929, 2002 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

