E2F1 mediates DNA damage and apoptosis through HCF-1 and the MLL family of histone methyltransferases
- PMID: 19763085
- PMCID: PMC2771094
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2009.258
E2F1 mediates DNA damage and apoptosis through HCF-1 and the MLL family of histone methyltransferases
Abstract
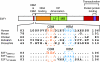
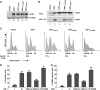
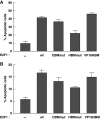
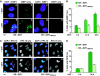
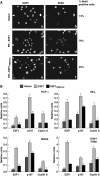
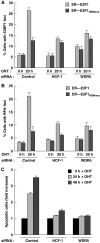
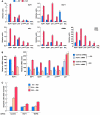
E2F1 is a key positive regulator of human cell proliferation and its activity is altered in essentially all human cancers. Deregulation of E2F1 leads to oncogenic DNA damage and anti-oncogenic apoptosis. The molecular mechanisms by which E2F1 mediates these two processes are poorly understood but are important for understanding cancer progression. During the G1-to-S phase transition, E2F1 associates through a short DHQY sequence with the cell-cycle regulator HCF-1 together with the mixed-lineage leukaemia (MLL) family of histone H3 lysine 4 (H3K4) methyltransferases. We show here that the DHQY HCF-1-binding sequence permits E2F1 to stimulate both DNA damage and apoptosis, and that HCF-1 and the MLL family of H3K4 methyltransferases have important functions in these processes. Thus, HCF-1 has a broader role in E2F1 function than appreciated earlier. Indeed, sequence changes in the E2F1 HCF-1-binding site can modulate both up and down the ability of E2F1 to induce apoptosis indicating that HCF-1 association with E2F1 is a regulator of E2F1-induced apoptosis.
Figures
References
-
- Bartek J, Bartkova J, Lukas J (2007) DNA damage signalling guards against activated oncogenes and tumour progression. Oncogene 26: 7773–7779 - PubMed
-
- Bartkova J, Horejsí Z, Koed K, Krämer A, Tort F, Zieger K, Guldberg P, Sehested M, Nesland JM, Lukas C, Ørntoft T, Lukas J, Bartek J (2005) DNA damage response as a candidate anti-cancer barrier in early human tumorigenesis. Nature 434: 864–870 - PubMed
-
- Bartkova J, Rezaei N, Liontos M, Karakaidos P, Kletsas D, Issaeva N, Vassiliou LV, Kolettas E, Niforou K, Zoumpourlis VC, Takaoka M, Nakagawa H, Tort F, Fugger K, Johansson F, Sehested M, Andersen CL, Dyrskjot L, Ørntoft T, Lukas J et al. (2006) Oncogene-induced senescence is part of the tumorigenesis barrier imposed by DNA damage checkpoints. Nature 444: 633–637 - PubMed
-
- Bates S, Phillips AC, Clark PA, Stott F, Peters G, Ludwig RL, Vousden KH (1998) p14ARF links the tumour suppressors RB and p53. Nature 395: 124–125 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

