Otitis media in a mouse model for Down syndrome
- PMID: 19765102
- PMCID: PMC2768146
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2613.2009.00677.x
Otitis media in a mouse model for Down syndrome
Abstract
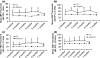
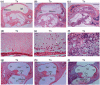
The Ts65Dn mouse shares many phenotypic characteristics of human Down syndrome. Here, we report that otitis media, characterized by effusion in the middle ear and hearing loss, was prevalent in Ts65Dn mice. Of the 53 Ts65Dn mice tested, 81.1% had high auditory-evoked brainstem response (ABR) thresholds for at least one of the stimulus frequencies (click, 8 kHz, 16 kHz and 32 kHz), in at least one ear. The ABR thresholds were variable and showed no tendency toward increase with age, from 2 to 7 months of age. Observation of pathology in mice, aged 3-4 months, revealed middle ear effusion in 11 of 15 Ts65Dn mice examined, but only in two of 11 wild-type mice. The effusion in each mouse varied substantially in volume and inflammatory cell content. The middle ear mucosae were generally thickened and goblet cells were distributed with higher density in the epithelium of the middle ear cavity of Ts65Dn mice as compared with those of wild-type controls. Bacteria of pathogenic importance to humans also were identified in the Ts65Dn mice. This is the first report of otitis media in the Ts65Dn mouse as a model characteristic of human Down syndrome.
Figures
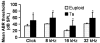

Similar articles
-
Ectopic Mineralization and Conductive Hearing Loss in Enpp1asj Mutant Mice, a New Model for Otitis Media and Tympanosclerosis.PLoS One. 2016 Dec 13;11(12):e0168159. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0168159. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27959908 Free PMC article.
-
Auditory function in the Tc1 mouse model of down syndrome suggests a limited region of human chromosome 21 involved in otitis media.PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e31433. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0031433. Epub 2012 Feb 14. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22348087 Free PMC article.
-
Hearing loss in a mouse model of 22q11.2 Deletion Syndrome.PLoS One. 2013 Nov 14;8(11):e80104. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0080104. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24244619 Free PMC article.
-
Early otitis media with effusion, hearing loss, and auditory processes at school age.Ear Hear. 2006 Aug;27(4):353-68. doi: 10.1097/01.aud.0000224727.45342.e9. Ear Hear. 2006. PMID: 16825885
-
Management of Conductive Hearing Loss in Children.Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2015 Dec;48(6):955-74. doi: 10.1016/j.otc.2015.06.007. Epub 2015 Sep 8. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2015. PMID: 26360369 Review.
Cited by
-
Auditory Phenotype and Histopathologic Findings of a Mutant Nlrp3 Expression Mouse Model.Front Neurol. 2022 Jun 24;13:890256. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.890256. eCollection 2022. Front Neurol. 2022. PMID: 35812087 Free PMC article.
-
Commonality in Down and fetal alcohol syndromes.Birth Defects Res A Clin Mol Teratol. 2013 Apr;97(4):187-97. doi: 10.1002/bdra.23129. Epub 2013 Apr 3. Birth Defects Res A Clin Mol Teratol. 2013. PMID: 23554291 Free PMC article.
-
Cilia distribution and polarity in the epithelial lining of the mouse middle ear cavity.Sci Rep. 2017 Mar 30;7:45870. doi: 10.1038/srep45870. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28358397 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling the genetics of otitis media: from mouse to human and back again.Mamm Genome. 2011 Feb;22(1-2):66-82. doi: 10.1007/s00335-010-9295-1. Epub 2010 Nov 25. Mamm Genome. 2011. PMID: 21107580 Review.
-
What have we learned from murine models of otitis media?Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2013 Oct;13(5):501-11. doi: 10.1007/s11882-013-0360-1. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2013. PMID: 23775349 Review.
References
-
- Akeson EC, Lambert JP, Narayanswami S, Gardiner K, Bechtel LJ, Davisson MT. Ts65Dn – localization of the translocation breakpoint and trisomic gene content in a mouse model for Down’s syndrome. Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 2001;93:270–276. - PubMed
-
- Balkany TJ, Downs MP, Jafek BW, Krajicek MJ. Hearing loss in Down’s syndrome. A treatable handicap more common than generally recognized. Clin. Pediatr. 1979;18:116–118. - PubMed
-
- Bilgin H, Kasemsuwan L, Schachern PA, Paparella MM, Le CT. Temporal bone study of Down’s syndrome. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 1996;122:271–275. - PubMed
-
- Blaser S, Propst EJ, Martin D, et al. Inner ear dysplasia is common in children with Down syndrome (trisomy 21) Laryngoscope. 2006;116:2113–2119. - PubMed
-
- Bleich A, Kirsch P, Sahly H, et al. Klebsiella oxytoca: opportunistic infections in laboratory rodents. Lab. Anim. 2008;42:369–375. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

