Suppressive effect of secretory phospholipase A2 inhibitory peptide on interleukin-1beta-induced matrix metalloproteinase production in rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts, and its antiarthritic activity in hTNFtg mice
- PMID: 19765281
- PMCID: PMC2787297
- DOI: 10.1186/ar2810
Suppressive effect of secretory phospholipase A2 inhibitory peptide on interleukin-1beta-induced matrix metalloproteinase production in rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts, and its antiarthritic activity in hTNFtg mice
Abstract
Introduction: Secretory phospholipase A2 (sPLA2) and matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) inhibitors are potent modulators of inflammation with therapeutic potential, but have limited efficacy in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). The objective of this study was to understand the inhibitory mechanism of phospholipase inhibitor from python (PIP)-18 peptide in cultured synovial fibroblasts (SF), and to evaluate its therapeutic potential in a human tumor necrosis factor (hTNF)-driven transgenic mouse (Tg197) model of arthritis.
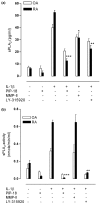
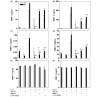
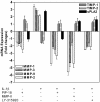
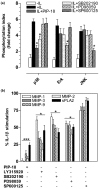
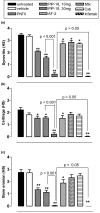
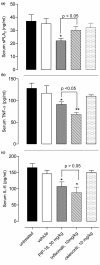
Methods: Gene and protein expression of sPLA2-IIA, MMP-1, MMP-2, MMP-3, MMP-9, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase (TIMP)-1, and TIMP-2 were analyzed by real time PCR and ELISA respectively, in interleukin (IL)-1beta stimulated rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and osteoarthritis (OA) synovial fibroblasts cells treated with or without inhibitors of sPLA2 (PIP-18, LY315920) or MMPs (MMP Inhibitor II). Phosphorylation status of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) proteins was examined by cell-based ELISA. The effect of PIP-18 was compared with that of celecoxib, methotrexate, infliximab and antiflamin-2 in Tg197 mice after ip administration (thrice weekly for 5 weeks) at two doses (10, 30 mg/kg), and histologic analysis of ankle joints. Serum sPLA2 and cytokines (tumor necrosis factor (TNF)alpha, IL-6) were measured by Escherichia coli (E coli) assay and ELISA, respectively.
Results: PIP-18 inhibited sPLA2-IIA production and enzymatic activity, and suppressed production of MMPs in IL-1beta-induced RA and OA SF cells. Treatment with PIP-18 blocked IL-1beta-induced p38 MAPK phosphorylation and resulted in attenuation of sPLA2-IIA and MMP mRNA transcription in RA SF cells. The disease modifying effect of PIP-18 was evidenced by significant abrogation of synovitis, cartilage degradation and bone erosion in hTNF Tg197 mice.
Conclusions: Our results demonstrate the benefit that can be gained from using sPLA2 inhibitory peptide for RA treatment, and validate PIP-18 as a potential therapeutic in a clinically relevant animal model of human arthritis.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The effects of 1 alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D(3) on matrix metalloproteinase and prostaglandin E(2) production by cells of the rheumatoid lesion.Arthritis Res. 1999;1(1):63-70. doi: 10.1186/ar12. Epub 1999 Oct 14. Arthritis Res. 1999. PMID: 11056661 Free PMC article.
-
Intercellular adhesion molecule-1 mediates the inhibitory effects of hyaluronan on interleukin-1beta-induced matrix metalloproteinase production in rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts via down-regulation of NF-kappaB and p38.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2006 Jul;45(7):824-32. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kel026. Epub 2006 Jan 31. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2006. PMID: 16449361
-
Retinoblastoma suppression of matrix metalloproteinase 1, but not interleukin-6, through a p38-dependent pathway in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts.Arthritis Rheum. 2004 Jan;50(1):78-87. doi: 10.1002/art.11482. Arthritis Rheum. 2004. PMID: 14730602
-
DPP4 reduces proinflammatory cytokine production in human rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts.J Cell Physiol. 2021 Dec;236(12):8060-8069. doi: 10.1002/jcp.30494. Epub 2021 Jun 30. J Cell Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34192347 Review.
-
Advanced application of stimuli-responsive drug delivery system for inflammatory arthritis treatment.Mater Today Bio. 2022 Feb 21;14:100223. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2022.100223. eCollection 2022 Mar. Mater Today Bio. 2022. PMID: 35243298 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Simiao Pill Attenuates Collagen-Induced Arthritis in Rats through Suppressing the ATX-LPA and MAPK Signalling Pathways.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019 Mar 14;2019:7498527. doi: 10.1155/2019/7498527. eCollection 2019. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019. PMID: 31001354 Free PMC article.
-
Insights on the molecular mechanism of anti-inflammatory effect of formula from Islamic traditional medicine: An in-silico study.J Tradit Complement Med. 2018 Oct 5;9(4):353-363. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcme.2018.09.004. eCollection 2019 Oct. J Tradit Complement Med. 2018. PMID: 31453132 Free PMC article.
-
Celecoxib: considerations regarding its potential disease-modifying properties in osteoarthritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2011;13(5):239. doi: 10.1186/ar3437. Epub 2011 Sep 21. Arthritis Res Ther. 2011. PMID: 21955617 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human iPSC-based disease modeling studies identify a common mechanistic defect and potential therapies for AMD and related macular dystrophies.Dev Cell. 2024 Dec 16;59(24):3290-3305.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2024.09.006. Epub 2024 Oct 2. Dev Cell. 2024. PMID: 39362220
-
Role of the NLRP3 inflammasome in the transient release of IL-1β induced by monosodium urate crystals in human fibroblast-like synoviocytes.J Inflamm (Lond). 2015 Apr 10;12:30. doi: 10.1186/s12950-015-0070-7. eCollection 2015. J Inflamm (Lond). 2015. PMID: 25897296 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bongartz TA, Sutton J, Sweeting MJ, Buchan I, Matteson EL, Montori V. Anti-TNF antibody therapy in rheumatoid arthritis and the risk of serious infections and malignancies: systematic review and meta-analysis of rare harmful effects in randomized controlled trials. JAMA. 2006;295:2275–2285. doi: 10.1001/jama.295.19.2275. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Masuda S, Murakami M, Komiyama K, Ishihara M, Ishikawa Y, Ishii T, Kudo I. Various secretory phospholipase A2 enzymes are expressed in rheumatoid arthritis and augment prostaglandin production in cultured synovial cells. FEBS J. 2005;272:655–672. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2004.04489.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Yedgar S, Cohen Y, Shoseyov D. Control of phospholipase A2 activities for the treatment of inflammatory conditions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006;1761:1373–1382. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

