Response to gefitinib and erlotinib in Non-small cell lung cancer: a restrospective study
- PMID: 19765296
- PMCID: PMC2758901
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-9-333
Response to gefitinib and erlotinib in Non-small cell lung cancer: a restrospective study
Abstract
Background: In Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), an overactive epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) pathway is a component of the malignant phenotype. Two tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) of EGFR, gefinitib and erlotinib, have been used with variable benefit.
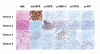
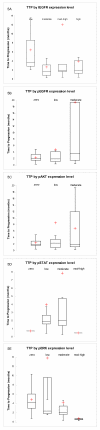
Methods: We have analyzed outcome data of a population of NSCLC patients that received these TKIs to determine the benefit derived and to define the clinical and molecular parameters that correlate with response. Tumor tissue from a subgroup of these patients was analyzed by immunohistochemistry to measure the expression level of EGFR and four activated (phosphorylated) members of the pathway, pEGFR, pERK, pAKT, and pSTAT3.
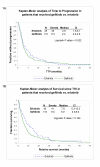
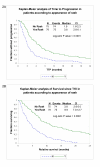
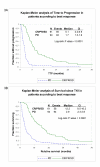
Results: Erlotinib was slightly superior to gefitinib in all measures of response, although the differences were not statistically significant. The most robust clinical predictors of time to progression (TTP) were best response and rash (p < 0.0001). A higher level of pEGFR was associated with longer TTP, while the total EGFR level was not associated with response. Higher levels of pAKT and pSTAT3 were also associated with longer TTP. In contrast, a higher level of pERK1/2 was associated with shorter TTP.
Conclusion: These observations suggest the hypothesis that tumor cells that have activated EGFR pathways, presumably being utilized for survival, are clinically relevant targets for pathway inhibition. An accurate molecular predictive model of TKI response should include activated members of the EGFR pathway. TKIs may be best reserved for tumors expressing pEGFR and pAKT or pSTAT, and little pERK. In the absence of molecular predictors of response, the appearance of a rash and a positive first scan are good clinical indicators of response.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of smoking status on progression-free and overall survival in non-small cell lung cancer patients receiving erlotinib or gefitinib: a meta-analysis.J Clin Pharm Ther. 2015 Dec;40(6):661-71. doi: 10.1111/jcpt.12332. Epub 2015 Nov 17. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2015. PMID: 26573867
-
Gefitinib or erlotinib in previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer patients: a cohort study in Taiwan.Cancer Med. 2017 Jul;6(7):1563-1572. doi: 10.1002/cam4.1121. Epub 2017 Jun 22. Cancer Med. 2017. PMID: 28639751 Free PMC article.
-
Primary resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer harboring TKI-sensitive EGFR mutations: an exploratory study.Ann Oncol. 2013 Aug;24(8):2080-7. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdt127. Epub 2013 Apr 4. Ann Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23559152
-
[The predictive value of EGFR status in non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with EGFR-TKIs].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2010 Apr;13(4):375-9. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2010.04.20. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2010. PMID: 20677568 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
Clinical impact of switching to a second EGFR-TKI after a severe AE related to a first EGFR-TKI in EGFR-mutated NSCLC.Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2012 Jun;42(6):528-33. doi: 10.1093/jjco/hys042. Epub 2012 Mar 28. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22457323
Cited by
-
Gefitinib provides similar effectiveness and improved safety than erlotinib for advanced non-small cell lung cancer: A meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 Apr;97(16):e0460. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000010460. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018. PMID: 29668619 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of effectiveness and adverse effects of gefitinib, erlotinib and icotinib among patients with non-small cell lung cancer: A network meta-analysis.Exp Ther Med. 2017 Nov;14(5):4017-4032. doi: 10.3892/etm.2017.5094. Epub 2017 Sep 1. Exp Ther Med. 2017. PMID: 29104622 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the HER/PI3K/AKT Family Signaling Network as a Predictive Biomarker of Pathologic Complete Response for Patients With Breast Cancer Treated With Neratinib in the I-SPY 2 TRIAL.JCO Precis Oncol. 2018 Aug 16;2:PO.18.00024. doi: 10.1200/PO.18.00024. eCollection 2018. JCO Precis Oncol. 2018. PMID: 32914002 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling of tumor progression in NSCLC and intrinsic resistance to TKI in loss of PTEN expression.PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e48004. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0048004. Epub 2012 Oct 24. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23133538 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylated EGFR expression may predict outcome of EGFR-TKIs therapy for the advanced NSCLC patients with wild-type EGFR.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2012 Aug 18;31(1):65. doi: 10.1186/1756-9966-31-65. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22901364 Free PMC article.
References
-
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer, Version 2. Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. 2008. http://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/f_guidelines.asp Accessed November 20, 2007.
-
- Hanna N, Shepherd FA, Fossella FV, Pereira JR, De Marinis F, von Pawel J, Gatzemeier U, Tsao TC, Pless M, Muller T, Lim HL, Desch C, Szondy K, Gervais R, Shaharyar, Manegold C, Paul S, Paoletti P, Einhorn L, Bunn PA Jr. Randomized phase III trial of pemetrexed versus docetaxel in patients with non-small cell lung cancer previously treated with chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22:1589–1597. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa050753. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Shepherd FA, Rodriguez Pereira J, Ciuleanu T, Tan EH, Hirsh V, Thongprasert S, Campos D, Maoleekoonpiroj S, Smylie M, Martins R, van Kooten M, Dediu M, Findlay B, Tu D, Johnston D, Bezjak A, Clark G, Santabárbara P, Seymour L. Erlotinib in previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:123–132. doi: 10.1016/S0169-5002(03)00137-5. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kim ES, Hirsh V, Mok T, Socinski MA, Gervais R, Wu YL, Li LY, Watkins CL, Sellers MV, Lowe ES, Sun Y, Liao ML, Osterlind K, Reck M, Armour AA, Shepherd FA, Lippman SM, Douillard JY. Gefitinib versus docetaxel in previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer (INTEREST): a randomised phase III trial. Lancet. 2008;372(9652):1809–18. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(08)61758-4. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

