Magnetic resonance imaging of multifunctional pluronic stabilized iron-oxide nanoparticles in tumor-bearing mice
- PMID: 19765817
- PMCID: PMC2763936
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2009.08.042
Magnetic resonance imaging of multifunctional pluronic stabilized iron-oxide nanoparticles in tumor-bearing mice
Abstract
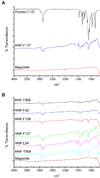
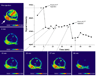
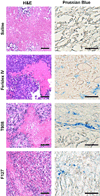
We are investigating the magnetic resonance imaging characteristics of magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) that consist of an iron-oxide magnetic core coated with oleic acid (OA), then stabilized with a pluronic or tetronic block copolymer. Since pluronics and tetronics vary structurally, and also in the ratio of hydrophobic (poly[propylene oxide]) and hydrophilic (poly[ethylene oxide]) segments in the polymer chain and in molecular weight, it was hypothesized that their anchoring to the OA coating around the magnetic core could significantly influence the physical properties of MNPs, their interactions with biological environment following intravenous administration, and ability to localize to tumors. The amount of block copolymer associated with MNPs was seen to depend upon their molecular structures and influence the characteristics of MNPs. Pluronic F127-modified MNPs demonstrated sustained and enhanced contrast in the whole tumor, whereas that of Feridex IV was transient and confined to the tumor periphery. In conclusion, our pluronic F127-coated MNPs, which can also be loaded with anticancer agents for drug delivery, can be developed as an effective cancer theranostic agent, i.e. an agent with combined drug delivery and imaging properties.
Figures


References
-
- Weber MA, Giesel FL, Stieltjes B. MRI for identification of progression in brain tumors: from morphology to function. Expert Rev Neurother. 2008;8:1507–1525. - PubMed
-
- Khoo VS, Joon DL. New developments in MRI for target volume delineation in radiotherapy. Br J Radiol. 2006;79(Spec No 1):S2–S15. - PubMed
-
- Xie J, Xu C, Kohler N, Hou Y, Sun S. Controlled PEGylation of monodisperse Fe3O4 nanoparticles for reduced non-specific uptake by macrophage cells. Adv Mater. 2007;19:3163–3166.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

