Genetic structure of Aedes aegypti in Australia and Vietnam revealed by microsatellite and exon primed intron crossing markers suggests feasibility of local control options
- PMID: 19769038
- PMCID: PMC2782737
- DOI: 10.1603/033.046.0514
Genetic structure of Aedes aegypti in Australia and Vietnam revealed by microsatellite and exon primed intron crossing markers suggests feasibility of local control options
Abstract
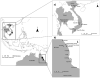
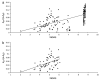
The distribution of Aedes aegypti (L.) in Australia is currently restricted to northern Queensland, but it has been more extensive in the past. In this study, we evaluate the genetic structure of Ae. aegypti populations in Australia and Vietnam and consider genetic differentiation between mosquitoes from these areas and those from a population in Thailand. Six microsatellites and two exon primed intron crossing markers were used to assess isolation by distance across all populations and also within the Australian sample. Investigations of founder effects, amount of molecular variation between and within regions and comparison of F(ST) values among Australian and Vietnamese populations were made to assess the scale of movement ofAe. aegypti. Genetic control methods are under development for mosquito vector populations including the dengue vector Ae. aegypti. The success of these control methods will depend on the population structure of the target species including population size and rates of movement among populations. Releases of modified mosquitoes could target local populations that show a high degree of isolation from surrounding populations, potentially allowing new variants to become established in one region with eventual dispersal to other regions.
Figures

References
-
- Atarhouch T, Rami M, Naciri M, Dakkak A. Genetic population structure of sardine (Sardina pilchardus) off Morocco detected with intron polymorphism (EPIC-PCR) Mar. Biol. 2007;150:521–528.
-
- Belkhir K, Borsa P, Chikhi L, Raufaste N, Bonhomme F. Laboratoire Génome, Populations, Interactions, CNRS UMR 5000. Université de Montpellier II; Montpellier, France: 2004. GENETIX 4.05, logiciel sous Windows TM pour la génétique des populations.
-
- Berrebi P, Retif X, Fang F, Zhang CG. Population structure and systematics of Opsariichthys bidens (Osteichthyes: Cyprinidae) in south-east China using a new nuclear marker: the introns (EPIC-PCR) Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2006;87:155–166.
-
- Bosio CF, Harrington LC, Jones JW, Sithiprasasna R, Norris DE, Scott TW. Genetic structure of Aedes aegypti populations in Thailand using mitochondrial DNA. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2005;72:434–442. - PubMed
-
- Chambers EW, Meece JK, McGowan JA, Lovin DD, Hemme RR, Chadee DD, McAbee K, Brown SE, Knudson DL, Severson DW. Microsatellite isolation and linkage group identification in the yellow fever mosquito Aedes aegypti. J. Hered. 2007;98:202–210. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

