A comparison of budesonide/formoterol maintenance and reliever therapy vs. conventional best practice in asthma management
- PMID: 19769705
- PMCID: PMC2780558
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1742-1241.2009.02185.x
A comparison of budesonide/formoterol maintenance and reliever therapy vs. conventional best practice in asthma management
Abstract
Objective: To study the effectiveness and safety of budesonide/formoterol (Symbicort) Maintenance And Reliever Therapy (Symbicort SMART, AstraZeneca, Södertalje, Sweden), a simplified management approach with one inhaler compared with conventional best practice (CBP) with multiple inhalers in patients with persistent asthma.
Design: Open-label randomised controlled parallel group trial, 6-month treatment.
Participants: A total of 908 patients > or = 12 years of age, with persistent asthma receiving treatment with inhaled corticosteroids (ICS), either alone or in conjunction with long-acting beta(2)-agonist.
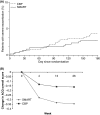
Main outcome measures: Time to first severe asthma exacerbation and number of severe asthma exacerbations.
Results: No difference between groups was seen in time to first severe exacerbation (p = 0.75). Exacerbation rates were low in both groups. A total of 12 patients in the Symbicort SMART group experienced a total of 14 severe asthma exacerbations, and 19 patients in the CBP group experienced a total of 25 severe asthma exacerbations (annual rate 0.07 vs. 0.13 p = 0.09). The mean daily dose of ICS expressed in BDP equivalent was significantly lower in the Symbicort SMART group (including as-needed use) vs. in the CBP group (749 microg vs. 1059 microg; p < 0.0001). Mean scores in Asthma Control Questionnaire, 5 question version improved significantly in the SMART group compared with the CBP group (p = 0.0026). Symbicort SMART and CBP were equally well tolerated. The mean drug cost/patient/month was significantly lower for the patients in the Symbicort SMART group compared with patients receiving CBP (51.3 euros vs. 66.5 euros; p < 0.0001).
Conclusions: In Belgian patients, a simplified regimen using budesonide/formoterol maintenance and reliever therapy was at least as effective at improving clinical control compared with CBP with a significantly lower ICS dose and significantly lower drug costs.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00290264.
Figures
References
-
- Global Initiative for Asthma. National Heart and Lung Institute, National Institutes of Health USA, and the world health Organization. http://www.ginasthma.org (accessed November 2006)
-
- Gibson PG, Saltos N, Fakes K. Acute anti-inflammatory effects of inhaled budesonide in asthma: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001;163:32–6. - PubMed
-
- Engel T, Dirksen A, Heinig JH, Nielsen NH, Weeke B, Johansson SA. Single-dose inhaled budesonide in subjects with chronic asthma. Allergy. 1991;46:547–53. - PubMed
-
- Pauwels RA, Lofdahl CG, Postma DS, et al. Effect of inhaled formoterol and budesonide on exacerbations of asthma. Formoterol and Corticosteroids Establishing Therapy (FACET) International Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1997;337:1405–11. - PubMed
-
- Zetterstrom O, Buhl R, Mellem H, et al. Improved asthma control with budesonide/formoterol in a single inhaler, compared with budesonide alone. Eur Respir J. 2001;18:262–8. - PubMed