Absence of heartbeat in the Xenopus tropicalis mutation muzak is caused by a nonsense mutation in cardiac myosin myh6
- PMID: 19769958
- PMCID: PMC2786259
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2009.09.019
Absence of heartbeat in the Xenopus tropicalis mutation muzak is caused by a nonsense mutation in cardiac myosin myh6
Abstract
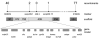
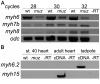
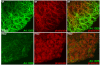
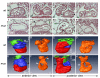
Mechanisms coupling heart function and cardiac morphogenesis can be accessed in lower vertebrate embryos that can survive to swimming tadpole stages on diffused oxygen. Forward genetic screens in Xenopus tropicalis have identified more than 80 mutations affecting diverse developmental processes, including cardiac morphogenesis and function. In the first positional cloning of a mutation in X. tropicalis, we show that non-contractile hearts in muzak (muz) embryos are caused by a premature stop codon in the cardiac myosin heavy chain gene myh6. The mutation deletes the coiled-coil domain responsible for polymerization into thick filaments, severely disrupting the cardiomyocyte cytoskeleton. Despite the lack of contractile activity and absence of a major structural protein, early stages of cardiac morphogenesis including looping and chamber formation are grossly normal. Muz hearts subsequently develop dilated chambers with compressed endocardium and fail to form identifiable cardiac valves and trabeculae.
Figures

References
-
- Beis D, et al. Genetic and cellular analyses of zebrafish atrioventricular cushion and valve development. Development. 2005;132:4193–204. - PubMed
-
- Branford WW, Essner JJ, Yost HJ. Regulation of gut and heart left-right asymmetry by context-dependent interactions between xenopus lefty and BMP4 signaling. Dev Biol. 2000;223:291–306. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

