Chronic inflammation and asthma
- PMID: 19769993
- PMCID: PMC2923754
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2009.09.005
Chronic inflammation and asthma
Abstract
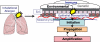
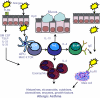
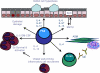
Allergic asthma is a complex and chronic inflammatory disorder which is associated with airway hyper-responsiveness and tissue remodelling of the airway structure. Although originally thought to be a Th2-driven inflammatory response to inhaled innocuous allergen, the immune response in asthma is now considered highly heterogeneous. There are now various in vivo systems which have been designed to examine the pathways leading to the development of this chronic immune response and reflect, in part this heterogeneity. Furthermore, the emergence of endogenous immunoregulatory pathways and active pro-resolving mediators hold great potential for future therapeutic intervention. In this review, the key cellular and molecular mediators relating to chronic allergic airway disease are discussed, as well as emerging players in the regulation of chronic allergic inflammation.
Copyright © 2009 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Holgate S.T., Polosa R. Treatment strategies for allergy and asthma. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008;8:218–230. - PubMed
-
- Nelson H.S. The importance of allergens in the development of asthma and the persistence of symptoms. Dis. Mon. 2001;47:5–15. - PubMed
-
- Holgate S.T., Davies D.E., Powell R.M., Howarth P.H., Haitchi H.M., Holloway J.W. Local genetic and environmental factors in asthma disease pathogenesis: chronicity and persistence mechanisms. Eur. Respir. J. 2007;29:793–803. - PubMed
-
- Karjalainen J., Hulkkonen J., Nieminen M.M., Huhtala H., Aromaa A., Klaukka T., Hurme M. Interleukin-10 gene promoter region polymorphism is associated with eosinophil count and circulating immunoglobulin E in adult asthma. Clin. Exp. Allergy. 2003;33:78–83. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

