Three stages of facial expression processing: ERP study with rapid serial visual presentation
- PMID: 19770052
- PMCID: PMC3794431
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.09.018
Three stages of facial expression processing: ERP study with rapid serial visual presentation
Abstract
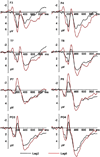
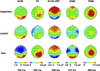
Electrophysiological correlates of the processing facial expressions were investigated in subjects performing the rapid serial visual presentation (RSVP) task. The peak latencies of the event-related potential (ERP) components P1, vertex positive potential (VPP), and N170 were 165, 240, and 240 ms, respectively. The early anterior N100 and posterior P1 amplitudes elicited by fearful faces were larger than those elicited by happy or neutral faces, a finding which is consistent with the presence of a 'negativity bias.' The amplitude of the anterior VPP was larger when subjects were processing fearful and happy faces than when they were processing neutral faces; it was similar in response to fearful and happy faces. The late N300 and P300 not only distinguished emotional faces from neutral faces but also differentiated between fearful and happy expressions in lag2. The amplitudes of the N100, VPP, N170, N300, and P300 components and the latency of the P1 component were modulated by attentional resources. Deficient attentional resources resulted in decreased amplitude and increased latency of ERP components. In light of these results, we present a hypothetical model involving three stages of facial expression processing.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Neural correlates of facial expression processing during a detection task: An ERP study.PLoS One. 2017 Mar 28;12(3):e0174016. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0174016. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28350800 Free PMC article.
-
The influence of spatial frequency content on facial expression processing: An ERP study using rapid serial visual presentation.Sci Rep. 2018 Feb 5;8(1):2383. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-20467-1. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29403062 Free PMC article.
-
Perceiving emotions in the eyes: The biasing role of a fearful mouth.Biol Psychol. 2025 Jan;194:108968. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsycho.2024.108968. Epub 2024 Dec 19. Biol Psychol. 2025. PMID: 39709097
-
The effect of fearful faces on the attentional blink is modulated by emotional task relevance: An event-related potential study.Neuropsychologia. 2021 Nov 12;162:108043. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2021.108043. Epub 2021 Oct 1. Neuropsychologia. 2021. PMID: 34600892
-
Emotional facial expressions evoke faster orienting responses, but weaker emotional responses at neural and behavioural levels compared to scenes: A simultaneous EEG and facial EMG study.Neuroimage. 2016 Jan 1;124(Pt A):931-946. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2015.09.065. Epub 2015 Oct 8. Neuroimage. 2016. PMID: 26453930
Cited by
-
Negative Impact of Sadness on Response Inhibition in Females: An Explicit Emotional Stop Signal Task fMRI Study.Front Behav Neurosci. 2020 Jul 24;14:119. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2020.00119. eCollection 2020. Front Behav Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32903296 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic neural processing of linguistic cues related to death.PLoS One. 2013 Jun 28;8(6):e67905. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0067905. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23840787 Free PMC article.
-
Attentional and emotional brain response to message framing in context of green marketing.Heliyon. 2020 Sep 23;6(9):e04912. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e04912. eCollection 2020 Sep. Heliyon. 2020. PMID: 33005782 Free PMC article.
-
Multimodal emotion processing in autism spectrum disorders: an event-related potential study.Dev Cogn Neurosci. 2013 Jan;3:11-21. doi: 10.1016/j.dcn.2012.08.005. Epub 2012 Sep 1. Dev Cogn Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23245216 Free PMC article.
-
Fearful faces evoke a larger C1 than happy faces in executive attention task: an event-related potential study.Neurosci Lett. 2012 Sep 27;526(2):118-21. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2012.08.011. Epub 2012 Aug 15. Neurosci Lett. 2012. PMID: 22910608 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adolphs R. Recognizing emotion from facial expressions: psychological and neurological mechanisms. Behav. Cogn. Neurosci. Rev. 2002a;1:21–62. - PubMed
-
- Adolphs R. Neural systems for recognizing emotion. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2002b;12:169–177. - PubMed
-
- Ashley V, Vuilleumier P, Swick D. Time course and specificity of event-related potentials to emotional expressions. NeuroReport. 2004;15:211–216. - PubMed
-
- Bar-Haim Y, Lamy D, Glickman S. Attentional bias in anxiety: A behavioral and ERP study. Brain Cogn. 2005;59:11–22. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

