Current views on type 2 diabetes
- PMID: 19770178
- PMCID: PMC2814170
- DOI: 10.1677/JOE-09-0260
Current views on type 2 diabetes
Abstract
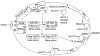
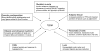
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) affects a large population worldwide. T2DM is a complex heterogeneous group of metabolic disorders including hyperglycemia and impaired insulin action and/or insulin secretion. T2DM causes dysfunctions in multiple organs or tissues. Current theories of T2DM include a defect in insulin-mediated glucose uptake in muscle, a dysfunction of the pancreatic beta-cells, a disruption of secretory function of adipocytes, and an impaired insulin action in liver. The etiology of human T2DM is multifactorial, with genetic background and physical inactivity as two critical components. The pathogenesis of T2DM is not fully understood. Animal models of T2DM have been proved to be useful to study the pathogenesis of, and to find a new therapy for, the disease. Although different animal models share similar characteristics, each mimics a specific aspect of genetic, endocrine, metabolic, and morphologic changes that occur in human T2DM. The purpose of this review is to provide the recent progress and current theories in T2DM and to summarize animal models for studying the pathogenesis of the disease.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interest that could be perceived as prejudicing the impartiality of the research reported.
Figures
References
-
- Abel ED, Peroni O, Kim JK, Kim YB, Boss O, Hadro E, Minnemann T, Shulman GI, Kahn BB. Adipose-selective targeting of the GLUT4 gene impairs insulin action in muscle and liver. Nature. 2001;409:729–733. - PubMed
-
- Accili D. Lilly lecture 2003: the struggle for mastery in insulin action: from triumvirate to republic. Diabetes. 2004;53:1633–1642. - PubMed
-
- Accili D, Drago J, Lee EJ, Johnson MD, Cool MH, Salvatore P, Asico LD, Jose PA, Taylor SI, Westphal H. Early neonatal death in mice homozygous for a null allele of the insulin receptor gene. Nature Genetics. 1996;12:106–109. - PubMed
-
- Aguirre V, Uchida T, Yenush L, Davis R, White MF. The c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase promotes insulin resistance during association with insulin receptor substrate-1 and phosphorylation of Ser(307) Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2000;275:9047–9054. - PubMed
-
- Aguirre V, Werner ED, Giraud J, Lee YH, Shoelson SE, White MF. Phosphorylation of Ser307 in insulin receptor substrate-1 blocks interactions with the insulin receptor and inhibits insulin action. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2002;277:1531–1537. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

