Kisspeptin signaling in the brain
- PMID: 19770291
- PMCID: PMC2761114
- DOI: 10.1210/er.2009-0005
Kisspeptin signaling in the brain
Abstract
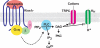
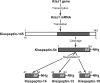
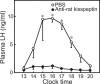
Kisspeptin (a product of the Kiss1 gene) and its receptor (GPR54 or Kiss1r) have emerged as key players in the regulation of reproduction. Mutations in humans or genetically targeted deletions in mice of either Kiss1 or Kiss1r cause profound hypogonadotropic hypogonadism. Neurons that express Kiss1/kisspeptin are found in discrete nuclei in the hypothalamus, as well as other brain regions in many vertebrates, and their distribution, regulation, and function varies widely across species. Kisspeptin neurons directly innervate and stimulate GnRH neurons, which are the final common pathway through which the brain regulates reproduction. Kisspeptin neurons are sexually differentiated with respect to cell number and transcriptional activity in certain brain nuclei, and some kisspeptin neurons express other cotransmitters, including dynorphin and neurokinin B (whose physiological significance is unknown). Kisspeptin neurons express the estrogen receptor and the androgen receptor, and these cells are direct targets for the action of gonadal steroids in both male and female animals. Kisspeptin signaling in the brain has been implicated in mediating the negative feedback action of sex steroids on gonadotropin secretion, generating the preovulatory GnRH/LH surge, triggering and guiding the tempo of sexual maturation at puberty, controlling seasonal reproduction, and restraining reproductive activity during lactation. Kisspeptin signaling may also serve diverse functions outside of the classical realm of reproductive neuroendocrinology, including the regulation of metastasis in certain cancers, vascular dynamics, placental physiology, and perhaps even higher-order brain function.
Figures


References
-
- Lee JH, Miele ME, Hicks DJ, Phillips KK, Trent JM, Weissman BE, Welch DR 1996 KiSS-1, a novel human malignant melanoma metastasis-suppressor gene. J Natl Cancer Inst 88:1731–1737 - PubMed
-
- Kotani M, Detheux M, Vandenbogaerde A, Communi D, Vanderwinden JM, Le Poul E, Brézillon S, Tyldesley R, Suarez-Huerta N, Vandeput F, Blanpain C, Schiffmann SN, Vassart G, Parmentier M 2001 The metastasis suppressor gene KiSS-1 encodes kisspeptins, the natural ligands of the orphan G protein-coupled receptor GPR54. J Biol Chem 276:34631–34636 - PubMed
-
- Muir AI, Chamberlain L, Elshourbagy NA, Michalovich D, Moore DJ, Calamari A, Szekeres PG, Sarau HM, Chambers JK, Murdock P, Steplewski K, Shabon U, Miller JE, Middleton SE, Darker JG, Larminie CG, Wilson S, Bergsma DJ, Emson P, Faull R, Philpott KL, Harrison DC 2001 AXOR12, a novel human G protein-coupled receptor, activated by the peptide KiSS-1. J Biol Chem 276:28969–28975 - PubMed
-
- Ohtaki T, Shintani Y, Honda S, Matsumoto H, Hori A, Kanehashi K, Terao Y, Kumano S, Takatsu Y, Masuda Y, Ishibashi Y, Watanabe T, Asada M, Yamada T, Suenaga M, Kitada C, Usuki S, Kurokawa T, Onda H, Nishimura O, Fujino M 2001 Metastasis suppressor gene KiSS-1 encodes peptide ligand of a G-protein-coupled receptor. Nature 411:613–617 - PubMed
-
- Clements MK, McDonald TP, Wang R, Xie G, O'Dowd BF, George SR, Austin CP, Liu Q 2001 FMRFamide-related neuropeptides are agonists of the orphan G-protein-coupled receptor GPR54. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 284:1189–1193 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

