The effect of combined antiretroviral therapy on the overall mortality of HIV-infected individuals
- PMID: 19770621
- PMCID: PMC2920287
- DOI: 10.1097/QAD.0b013e3283324283
The effect of combined antiretroviral therapy on the overall mortality of HIV-infected individuals
Abstract
Objective: To estimate the effect of combined antiretroviral therapy (cART) on mortality among HIV-infected individuals after appropriate adjustment for time-varying confounding by indication.
Design: A collaboration of 12 prospective cohort studies from Europe and the United States (the HIV-CAUSAL Collaboration) that includes 62 760 HIV-infected, therapy-naive individuals followed for an average of 3.3 years. Inverse probability weighting of marginal structural models was used to adjust for measured confounding by indication.
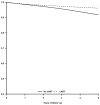
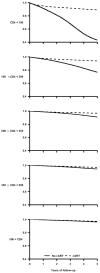
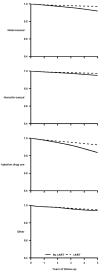
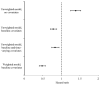
Results: Two thousand and thirty-nine individuals died during the follow-up. The mortality hazard ratio was 0.48 (95% confidence interval 0.41-0.57) for cART initiation versus no initiation. In analyses stratified by CD4 cell count at baseline, the corresponding hazard ratios were 0.29 (0.22-0.37) for less than 100 cells/microl, 0.33 (0.25-0.44) for 100 to less than 200 cells/microl, 0.38 (0.28-0.52) for 200 to less than 350 cells/microl, 0.55 (0.41-0.74) for 350 to less than 500 cells/microl, and 0.77 (0.58-1.01) for 500 cells/microl or more. The estimated hazard ratio varied with years since initiation of cART from 0.57 (0.49-0.67) for less than 1 year since initiation to 0.21 (0.14-0.31) for 5 years or more (P value for trend <0.001).
Conclusion: We estimated that cART halved the average mortality rate in HIV-infected individuals. The mortality reduction was greater in those with worse prognosis at the start of follow-up.
Figures
References
-
- Gulick RM, Mellors JW, Havlir D, et al. Treatment with indinavir, zidovudine, and lamivudine in adults with human immunodeficiency virus infection and prior antiretroviral therapy. N Engl J Med. 1997 Sep 11;337(11):734–739. - PubMed
-
- Hammer SM, Squires KE, Hughes MD, et al. A controlled trial of two nucleoside analogues plus indinavir in persons with human immunodeficiency virus infection and CD4 cell counts of 200 per cubic millimeter or less. AIDS Clinical Trials Group 320 Study Team. N Engl J Med. 1997 Sep 11;337(11):725–733. - PubMed
-
- Cole SR, Hernán MA, Robins JM, et al. Effect of highly active antiretroviral therapy on time to acquired immunodeficiency syndrome or death using marginal structural models. Am J Epidemiol. 2003 Oct 1;158(7):687–694. - PubMed
-
- Egger M, May M, Chene G, et al. Prognosis of HIV-1-infected patients starting highly active antiretroviral therapy: a collaborative analysis of prospective studies. Lancet. 2002 Jul 13;360(9327):119–129. - PubMed
-
- Cameron DW, Heath-Chiozzi M, Danner S, et al. Randomised placebo-controlled trial of ritonavir in advanced HIV-1 disease. The Advanced HIV Disease Ritonavir Study Group. Lancet. 1998 Feb 21;351(9102):543–549. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

