Frog Prince transposon-based RNAi vectors mediate efficient gene knockdown in human cells
- PMID: 19771210
- PMCID: PMC2737204
Frog Prince transposon-based RNAi vectors mediate efficient gene knockdown in human cells
Abstract
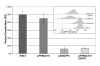
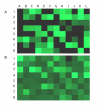
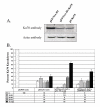
We have developed a stable RNA interference (RNAi) delivery system that is based on the Frog Prince transposable element. This plasmid-based vector system combines the gene silencing capabilities of H1 polymerase III promoter-driven short hairpin RNAs (shRNA) with the advantages of stable and efficient genomic integration of the shRNA cassette mediated by transposition. We show that the Frog Prince-based shRNA expressing system can efficiently knock down the expression of both exogenous as well as endogenous genes in human cells. Furthermore, we use the Frog Prince-based system to study the effect of knockdown of the DNA repair factor Ku70 on transposition of the Sleeping Beauty transposon. Transposon-mediated genomic integration ensures that the shRNA expression cassette and a selectable marker gene within the transposon remain intact and physically linked. We demonstrate that a major advantage of our vector system over plasmid-based shRNA delivery is both its enhanced frequency of intact genomic integration as well as higher target suppression in transgenic human cells. Due to its simplicity and effectiveness, transposon-based RNAi is an emerging tool to facilitate analysis of gene function through the establishment of stable loss-of-function cell lines.
Keywords: Frog Prince; RNA interference; Sleeping Beauty; nonviral gene transfer; short hairpin RNA; stable gene knockdown; transposon-based gene delivery.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Abbas-Terki T, Blanco-Bose W, Deglon N, Pralong W, Aebischer P. Lentiviral-mediated RNA interference. Hum Gene Ther. 2002;13:2197–2201. - PubMed
-
- Bishop JO. Chromosomal insertion of foreign DNA. Reprod Nutr Dev. 1996;36:607–618. - PubMed
-
- Brummelkamp TR, Bernards R, Agami R. A system for stable expression of short interfering RNAs in mammalian cells. Science. 2002;296:550–553. - PubMed
-
- Caplen NJ. Gene therapy progress and prospects. Downregulating gene expression: the impact of RNA interference. Gene Ther. 2004;11:1241–1248. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
