Resveratrol at high doses acts as an apoptotic inducer in endothelial cells
- PMID: 19771259
- PMCID: PMC2741653
- DOI: 10.4143/crt.2006.38.1.48
Resveratrol at high doses acts as an apoptotic inducer in endothelial cells
Abstract
Purposes: Resveratrol is a phenolic compound found in grapes and other food products. In order to assess the availability of resveratrol as an angio-inhibiting drug, we examined whether resveratrol plays an important role in bovine aortic endothelial cells (BAECs) for cell apoptosis and cell migration.
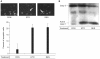
Methods and materials: Endothelial cell apoptosis was observed as detected by the Hoechst staining and the caspase-3 activity. Additionally, Western blotting was performed for monitoring the activities of various cell signaling molecules.
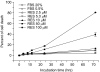
Results: Resveratrol was shown to act as a pro-apoptotic agent. The pro-apoptotic effect of resveratrol was as great as that of etoposide, a well-known anti-cancer drug. In addition, resveratrol had an inhibitory effect on endothelial cell migration. The demonstrated efficacy of resveratrol suggests that resveratrol may be utilized as an anti-angiogenic drug. To determine the underlying mechanisms, we further investigated which signaling molecules are activated by resveratrol. Extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) was activated by the treatment with resveratrol in BAECs, whereas endothelial nitric oxide synthetase (eNOS), Akt, and Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) were inhibited. The pretreatment with PD compound, an ERK inhibitor, had no effect on the pro-apoptosis induced by resveratrol.
Conclusion: Resveratrol plays an important role in endothelial cell apoptosis, indicating that resveratrol can be utilized as a potent anti-angiogenic drug.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Caspase-3; Cell signaling; Endothelial cells; Resveratrol.
Figures


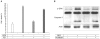
Similar articles
-
Resveratrol induces FasL-related apoptosis through Cdc42 activation of ASK1/JNK-dependent signaling pathway in human leukemia HL-60 cells.Carcinogenesis. 2005 Jan;26(1):1-10. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgh220. Epub 2004 Jun 24. Carcinogenesis. 2005. PMID: 15217905
-
Resveratrol at anti-angiogenesis/anticancer concentrations suppresses protein kinase G signaling and decreases IAPs expression in HUVECs.Anticancer Res. 2015 Jan;35(1):273-81. Anticancer Res. 2015. PMID: 25550561
-
Pinosylvin induces cell survival, migration and anti-adhesiveness of endothelial cells via nitric oxide production.Phytother Res. 2013 Apr;27(4):610-7. doi: 10.1002/ptr.4770. Epub 2012 Jun 27. Phytother Res. 2013. PMID: 22736379
-
FERM domain promotes resveratrol-induced apoptosis in endothelial cells via inhibition of NO production.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013 Nov 29;441(4):891-6. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.10.154. Epub 2013 Nov 6. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013. PMID: 24211585
-
Resveratrol improves sperm parameter and testicular apoptosis in cisplatin-treated rats: Effects on ERK1/2, JNK, and Akt pathways.Syst Biol Reprod Med. 2019 Jun;65(3):236-249. doi: 10.1080/19396368.2018.1541114. Epub 2018 Dec 3. Syst Biol Reprod Med. 2019. PMID: 30507263
Cited by
-
Resveratrol exerts dosage and duration dependent effect on human mesenchymal stem cell development.PLoS One. 2012;7(5):e37162. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0037162. Epub 2012 May 16. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22615926 Free PMC article.
-
Resveratrol synergistically augments anti-tumor effect of 5-FU in vitro and in vivo by increasing S-phase arrest and tumor apoptosis.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2015 Dec;240(12):1672-81. doi: 10.1177/1535370215573396. Epub 2015 Mar 2. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2015. PMID: 25736303 Free PMC article.
-
Resveratrol promotes endothelial cell wound healing under laminar shear stress through an estrogen receptor-α-dependent pathway.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2014 Mar;306(6):H797-806. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00892.2013. Epub 2014 Jan 24. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24464753 Free PMC article.
-
Autophagy inhibition augments resveratrol-induced apoptosis in Ishikawa endometrial cancer cells.Oncol Lett. 2016 Oct;12(4):2560-2566. doi: 10.3892/ol.2016.4978. Epub 2016 Aug 8. Oncol Lett. 2016. PMID: 27698828 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Effects of Resveratrol on TNF-α-Induced Endothelial Cytotoxicity in Baboon Femoral Arterial Endothelial Cells.J Diabetes Res. 2013;2013:185172. doi: 10.1155/2013/185172. Epub 2013 Mar 31. J Diabetes Res. 2013. PMID: 23671856 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gasparini G. The rationale and future potential of angiogenesis inhibitors in neoplasia. Drugs. 1999;58:17–38. - PubMed
-
- Jang M, Cai L, Udeani GO, Slowing KV, Thomas CF, Beecher CW, et al. Cancer Chemopreventive activity of resveratrol, a natural product derived from grapes. Science. 1997;275:218–220. - PubMed
-
- Signorelli P, Ghidoni R. Resveratrol as an anticancer nutrient: molecular basis, open questions and promises. J Nutr Biochem. 2005;16:449–466. - PubMed
-
- Klinge CM, Blankenship KA, Resinger KE, Bhatnagar S, Noisin EL, Sumanasekera WK, et al. Resveratrol and estradiol rapidly activate MAPK signaling through estrogen receptors α and β in endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:7460–7468. - PubMed
-
- Jo H, Sipos K, Go YM, Law R, Rong J, McDonald JM. Differential effect of shear stress on extracellular signal-regulated kinase and N-terminal Jun kinase in endothelial cells. Gi2- and Gbeta/gamma-dependent signaling pathways. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:1395–1401. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

