AKAP12alpha is associated with promoter methylation in lung cancer
- PMID: 19771275
- PMCID: PMC2741672
- DOI: 10.4143/crt.2006.38.3.144
AKAP12alpha is associated with promoter methylation in lung cancer
Abstract
Purpose: Promoter methylation is an important mechanism for silencing tumor-suppressor genes in cancer and it is a promising tool for the development of molecular biomarkers. The purpose of the present study was to investigate whether inactivation of the A Kinase Anchoring Protein 12 (AKAP12) gene is assoCiated with promoter methylation in lung cancer.
Materials and methods: The AKAP12 expression was examined by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) in ten lung cancer cell lines. The methylation status of the AKAP12alpha promoter was analyzed by performing bisulfite sequencing analysis in ten lung cancer cell lines, twenty four lung tissues and matched normal tissues.
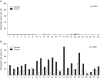
Results: The AKAP12alpha expression was reduced in 6 of 10 (60%) lung cancer cell lines, whereas the AKAP12beta expression was absent in 1 of 10 (10%) lung cancer cell lines. The AKAP12alpha expression was restored after treatment with the demethylating agent 5-aza-2'-deoxycytidine in three lung cancer cell lines. Methylation of CpG island 1 in the AKAP12alpha promoter was detected in 30% of the lung cancer cell lines, whereas methylation of CpG island 2 in the AKAP12alpha promoter was observed in the immortalized bronchial cell line and in all the lung cancer cell lines. In lung tumors, the CpG island 1 in the AKAP12alpha promoter was infrequently methylated. However, CpG island 2 in the AKAP12alpha promoter was highly methylated in lung tumors compared with the surrounding normal tissues, and this was statistically significant (p=0.0001).
Conclusion: Our results suggest that inactivation of the AKAP12alpha expression is assoCiated with DNA methylation of the promoter region in lung cancer, and that AKAP12alpha may play an important role in lung cancer carcinogenesis.
Keywords: AKAP12α; Lung neoplasms; Promoter methylation.
Figures



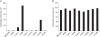
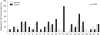
Similar articles
-
Methylation of AKAP12{alpha} promoter in lung cancer.Anticancer Res. 2010 Nov;30(11):4595-600. Anticancer Res. 2010. PMID: 21115911
-
Epigenetic silencing of AKAP12 in juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia.Epigenetics. 2016;11(2):110-9. doi: 10.1080/15592294.2016.1145327. Epub 2016 Feb 18. Epigenetics. 2016. PMID: 26891149 Free PMC article.
-
CpG island promoter methylation and silencing of 14-3-3sigma gene expression in LNCaP and Tramp-C1 prostate cancer cell lines is associated with methyl-CpG-binding protein MBD2.Oncogene. 2006 Aug 3;25(33):4559-72. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1209462. Epub 2006 Jun 19. Oncogene. 2006. PMID: 16786000 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic inactivation of laminin-5-encoding genes in lung cancers.Clin Cancer Res. 2003 Jul;9(7):2665-72. Clin Cancer Res. 2003. PMID: 12855645
-
DNA methylation paradigm shift: 15-lipoxygenase-1 upregulation in prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia and prostate cancer by atypical promoter hypermethylation.Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2007 Jan;82(1-4):185-97. doi: 10.1016/j.prostaglandins.2006.05.015. Epub 2006 Jul 11. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2007. PMID: 17164146
Cited by
-
CancerMA: a web-based tool for automatic meta-analysis of public cancer microarray data.Database (Oxford). 2012 Dec 15;2012:bas055. doi: 10.1093/database/bas055. Print 2012. Database (Oxford). 2012. PMID: 23241162 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of potential regulatory function of breast cancer risk locus at 6q25.1.Carcinogenesis. 2016 Feb;37(2):163-168. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgv170. Epub 2015 Dec 8. Carcinogenesis. 2016. PMID: 26645718 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging Roles for SSeCKS/Gravin/AKAP12 in the Control of Cell Proliferation, Cancer Malignancy, and Barriergenesis.Genes Cancer. 2010 Nov;1(11):1147-56. doi: 10.1177/1947601910392984. Genes Cancer. 2010. PMID: 21779438 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of tumor and metastasis progression through the scaffolding functions of SSeCKS/Gravin/AKAP12.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2012 Dec;31(3-4):493-500. doi: 10.1007/s10555-012-9360-1. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2012. PMID: 22684366 Free PMC article. Review.
-
FGF10 Triggers De Novo Alveologenesis in a Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia Model: Impact on Resident Mesenchymal Niche Cells.Stem Cells. 2022 Jun 22;40(6):605-617. doi: 10.1093/stmcls/sxac025. Stem Cells. 2022. PMID: 35437594 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Parkin DM, Bray FI, Devesa SS. Cancer burden in the year 2000. The global picture. Eur J Cancer. 2001;37(Suppl 8):S4–S66. - PubMed
-
- Kim HK. Lung cancer in Korea. Cancer Res Treat. 2002;34:1–2. - PubMed
-
- Jones PA, Baylin SB. The fundamental role of epigenetic events in cancer. Nat Rev Genet. 2002;3:415–428. - PubMed
-
- Herman JG, Baylin SB. Gene silencing in cancer in association with promoter hypermethylation. N Engl J Med. 2003;349:2042–2054. - PubMed
-
- Doerfler W. DNA methylation and gene activity. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:93–124. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

