The role of integrin alpha(v)beta (8) in neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury
- PMID: 19771486
- PMCID: PMC2847421
- DOI: 10.1007/s12640-009-9117-y
The role of integrin alpha(v)beta (8) in neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury
Abstract
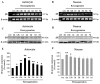
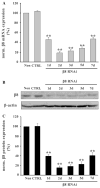
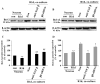
Integrin alpha(v)beta(8) plays an important role in cerebral vascular development. It has been proven that alpha(v)beta(8) is a key factor for transforming growth factor-beta1 (TGF-beta1) activation in epithelial cells. However, it is not clear whether alpha(v)beta(8) can activate TGF-beta1 and play a role in protection during neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury. In this study, we investigated the relationship between alpha(v)beta(8) and TGF-beta1 activation, and thus the effects of TGF-beta1 activation in the protection of neurons after hypoxia-ischemia (HI). Astrocytes and neurons from rat brains were cultured and then subjected to oxygen-glucose deprivation to generate HI model in vitro. beta(8) expression was determined using immunocytochemistry, western blot, and reverse-transcriptase polymerase chain reaction. TGF-beta1 activation was determined by TGF-beta bioassay in a tested cell (astrocyte) and a reporter cell co-culture system. The pro-apoptotic protein, cleaved caspase-3, and the anti-apoptotic protein, Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL, were detected using western blot. Cellular apoptosis was detected with TUNEL. We found that beta(8) expression was stronger in astrocytes than that in neurons under normoxia. HI resulted in a rapid and persistent increase of beta(8) expression in astrocytes, but only in a slight and transient increase in neurons. Astrocytes beta(8) could induce TGF-beta1 leading to upregulation of Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL, and thus attenuated neuronal apoptosis. The present findings suggest that beta(8) protecting the brain against neonatal HI injury through TGF-beta1 signaling pathway, which may have implications for the treatment of HI brain injury.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Integrin β8 signaling in neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury.Neurotox Res. 2012 Nov;22(4):280-91. doi: 10.1007/s12640-012-9312-0. Epub 2012 Jan 25. Neurotox Res. 2012. PMID: 22274870
-
[Effect of integrin beta8 on neuronal apoptosis after hypoxia ischemia in astrocyte/neuron co-culture system].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2014 Mar;28(3):366-70. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2014. PMID: 24844022 Chinese.
-
[Effect of integrin β8 on TGF-β1 activation in astrocytes with oxygen glucose deprivation].Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2014 Jan;16(1):73-6. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2014. PMID: 24461183 Chinese.
-
Protection of ischemic brain cells is dependent on astrocyte-derived growth factors and their receptors.Exp Neurol. 2006 Sep;201(1):225-33. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2006.04.014. Exp Neurol. 2006. PMID: 16765947
-
Transforming growth factor-beta: a neuroprotective factor in cerebral ischemia.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2003;39(1):13-22. doi: 10.1385/CBB:39:1:13. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2003. PMID: 12835526 Review.
Cited by
-
Danhong injection: A modulator for Golgi structural stability after cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury.Neural Regen Res. 2013 Sep 5;8(25):2343-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5374.2013.25.005. Neural Regen Res. 2013. PMID: 25206544 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiac endothelial cell-derived exosomes induce specific regulatory B cells.Sci Rep. 2014 Dec 23;4:7583. doi: 10.1038/srep07583. Sci Rep. 2014. PMID: 25533220 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of YB1 in Renal Cell Carcinoma Cell Adhesion.Int J Med Sci. 2018 Aug 6;15(12):1304-1311. doi: 10.7150/ijms.25580. eCollection 2018. Int J Med Sci. 2018. PMID: 30275756 Free PMC article.
-
14-3-3gamma and neuroglobin are new intrinsic protective factors for cerebral ischemia.Mol Neurobiol. 2010 Jun;41(2-3):218-31. doi: 10.1007/s12035-010-8142-4. Epub 2010 May 14. Mol Neurobiol. 2010. PMID: 20467836 Review.
-
Integrin β8 signaling in neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury.Neurotox Res. 2012 Nov;22(4):280-91. doi: 10.1007/s12640-012-9312-0. Epub 2012 Jan 25. Neurotox Res. 2012. PMID: 22274870
References
-
- Asano Y, Ihn H, Yamane K, Jinnin M, Mimura Y, Tamaki K. Increased expression of integrin alpha(v)beta3 contributes to the establishment of autocrine TGF-beta signaling in scleroderma fibroblasts. J Immunol. 2005a;175:7708–7718. - PubMed
-
- Asano Y, Ihn H, Yamane K, Jinnin M, Mimura Y, Tamaki K. Involvement of alphavbeta5 integrin-mediated activation of latent transforming growth factor beta1 in autocrine transforming growth factor beta signaling in systemic sclerosis fibroblasts. Arthritis Rheum. 2005b;52:2897–2905. - PubMed
-
- Bader BL, Rayburn H, Crowley D, Hynes RO. Extensive vasculogenesis, angiogenesis, and organogenesis precede lethality in mice lacking all alphav integrin. Cell. 1998;95:507–519. - PubMed
-
- Boche D, Cunningham C, Gauldie J, Perry VH. Transforming growth factor-beta 1-mediated neuroprotection against excitotoxic injury in vivo. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2003;23:1174–1182. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

