The role of toll-like receptors in rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 19772831
- PMCID: PMC2913446
- DOI: 10.1007/s11926-009-0051-z
The role of toll-like receptors in rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
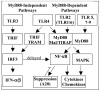
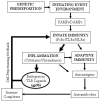
An increasing body of data supports the role of the innate immune system in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Toll-like receptors (TLRs) are expressed by cells within the RA joint and various endogenous TLR ligands are present within the inflamed joints of patients with RA. Further, various animal models suggest that TLR signaling is important in the pathogenesis of disease. Overall, the data suggest that activation by endogenous TLR ligands may contribute to the persistent expression of proinflammatory cytokines by macrophages and the joint damage to cartilage and bone that occurs in RA. The data support a potential role for suppression of TLR signaling as a novel therapeutic approach in patients with RA.
Figures
References
-
- Wijbrandts CA, Vergunst CE, Haringman JJ, Gerlag DM, Smeets TJ, Tak PP. Absence of changesn the number of synovial sublining macrophages after ineffective treatment for rheumatoid arthritis: Implications for use of synovial sublining macrophages as a biomarker. Arthritis Rheum. 2007;56(11):3869–71. Sublining macrophages are a biomarker for clinical response in RA. - PubMed
-
- Akira S, Uematsu S, Takeuchi O. Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell. 2006;124(4):783–801. - PubMed
-
- Iwahashi M, Yamamura M, Aita T, Okamoto A, Ueno A, Ogawa N, et al. Expression of Toll-like receptor 2 on CD16+ blood monocytes and synovial tissue macrophages in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2004;50(5):1457–67. - PubMed
-
- Sorensen LK, Havemose-Poulsen A, Sonder SU, Bendtzen K, Holmstrup P. Blood cell gene expression profiling in subjects with aggressive periodontitis and chronic arthritis. J Periodontol. 2008;79(3):477–85. - PubMed
-
- Radstake TR, Roelofs MF, Jenniskens YM, Oppers-Walgreen B, van Riel PL, Barrera P, et al. Expression of toll-like receptors 2 and 4 in rheumatoid synovial tissue and regulation by proinflammatory cytokines interleukin-12 and interleukin-18 via interferon-gamma. Arthritis Rheum. 2004;50(12):3856–65. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
