Direct bone formation during distraction osteogenesis does not require TNFalpha receptors and elevated serum TNFalpha fails to inhibit bone formation in TNFR1 deficient mice
- PMID: 19772956
- PMCID: PMC2818239
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bone.2009.09.011
Direct bone formation during distraction osteogenesis does not require TNFalpha receptors and elevated serum TNFalpha fails to inhibit bone formation in TNFR1 deficient mice
Abstract
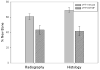
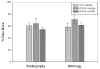
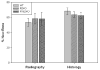
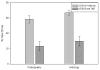
Distraction osteogenesis (DO) is a process which induces direct new bone formation as a result of mechanical distraction. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF) is a cytokine that can modulate osteoblastogenesis. The direct effects of TNF on direct bone formation in rodents are hypothetically mediated through TNF receptor 1 and/or 2 (TNFR1/2) signaling. We utilized a unique model of mouse DO to assess the effects of 1) TNFR homozygous null gene alterations on direct bone formation and 2) rmTNF on wild type (WT), TNFR1(-/-) (R1KO), and TNR2(-/-) (R2KO) mice. Radiological and histological analyses of direct bone formation in the distraction gaps demonstrated no significant differences between the WT, R1KO, R2KO, or TNFR1(-/-) and R2(-/-) (R1 and 2KO) mice. R1 and 2KO mice had elevated levels of serum TNF but demonstrated no inhibition of new bone formation. Systemic administration by osmotic pump of rmTNF during DO (10 microg/kg/day) resulted in significant inhibition of gap bone formation measures in WT and R2KO mice, but not in R1KO mice. We conclude that exogenous rmTNF and/or endogenous TNF act to inhibit new bone formation during DO by signaling primarily through TNFR1.
(c) 2009 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Distraction osteogenesis in TNF receptor 1 deficient mice is protected from chronic ethanol exposure.Alcohol. 2012 Mar;46(2):133-8. doi: 10.1016/j.alcohol.2011.08.007. Epub 2011 Sep 10. Alcohol. 2012. PMID: 21908154 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic ethanol exposure inhibits distraction osteogenesis in a mouse model: role of the TNF signaling axis.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2007 May 1;220(3):302-10. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2007.02.011. Epub 2007 Feb 24. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17391719 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor necrosis factor-alpha is toxic via receptor 1 and protective via receptor 2 in a murine model of myocardial infarction.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2007 Jul;293(1):H743-53. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00166.2007. Epub 2007 Apr 6. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17416608
-
Prothrombotic effects of tumor necrosis factor alpha in vivo are amplified by the absence of TNF-alpha receptor subtype 1 and require TNF-alpha receptor subtype 2.Arthritis Res Ther. 2012 Oct 18;14(5):R225. doi: 10.1186/ar4064. Arthritis Res Ther. 2012. PMID: 23079185 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the Interaction of Tumor Necrosis Factor-α and Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptors 1 and 2 in Bone-Related Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 27;23(3):1481. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031481. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163403 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Rosiglitazone disrupts endosteal bone formation during distraction osteogenesis by local adipocytic infiltration.Bone. 2013 Jan;52(1):247-58. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2012.09.038. Epub 2012 Oct 13. Bone. 2013. PMID: 23069375 Free PMC article.
-
Progranulin Promotes Regeneration of Inflammatory Periodontal Bone Defect in Rats via Anti-inflammation, Osteoclastogenic Inhibition, and Osteogenic Promotion.Inflammation. 2019 Feb;42(1):221-234. doi: 10.1007/s10753-018-0886-4. Inflammation. 2019. PMID: 30187338
-
Inhibin A enhances bone formation during distraction osteogenesis.J Orthop Res. 2012 Feb;30(2):288-95. doi: 10.1002/jor.21501. Epub 2011 Aug 1. J Orthop Res. 2012. PMID: 21809377 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of NF-κB activation by gentian violet promotes osteoblastogenesis and suppresses osteoclastogenesis.Curr Mol Med. 2014;14(6):783-92. doi: 10.2174/1566524014666140724104842. Curr Mol Med. 2014. PMID: 25056540 Free PMC article.
-
The role of PGRN in musculoskeletal development and disease.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2014 Jan 1;19(4):662-71. doi: 10.2741/4234. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2014. PMID: 24389211 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Nanes MS. Tumor necrosis factor-α: molecular and cellular mechanisms in skeletal pathology. Gene. 2003;321:1–15. - PubMed
-
- Frost A, Jonsson K, Nilsson O, Ljunggren O. Inflammatory cytokines regulate proliferation of cultured human osteoblasts. Acta Ortho Scand. 1997;68:91–96. - PubMed
-
- Gerstenfeld L, Cho T, Kon T, Aizawa T, Cruceta J, Graves B, Einhorn T. Impaired intramembranous bone formation during bone repair in the absence of tumor necrosis factor-alpha signaling. Cells Tissues Organs. 2001;169:285–294. - PubMed
-
- Gerstenfeld LC, Cho TJ, Kon T, Aizawa T, Tsay A, Fitch J, Barnes GL, Graves DT, Einhorn TA. Impaired fracture healing in the absence of TNF-alpha signaling: the role of TNF-alpha in endochondral cartilage resorption. J Bone Miner Res. 2003;18:1584–92. - PubMed
-
- Lehmann W, Edgar CM, Wang K, Cho TJ, Barnes GL, Kakar S, Graves DT, Rueger JM, Gerstenfeld LC, Einhorn TA. TNF alpha coordinately regulates the expression of specific matrix metalloproteinases and angiogenic factors during fracture healing. Bone. 2005;36:300–310. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

