Noninvasive imaging and radiovirotherapy of prostate cancer using an oncolytic measles virus expressing the sodium iodide symporter
- PMID: 19773744
- PMCID: PMC2810133
- DOI: 10.1038/mt.2009.218
Noninvasive imaging and radiovirotherapy of prostate cancer using an oncolytic measles virus expressing the sodium iodide symporter
Abstract
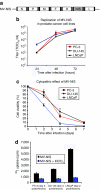
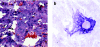
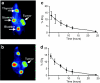
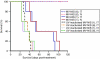
Prostate cancer cells overexpress the measles virus (MV) receptor CD46. Herein, we evaluated the antitumor activity of an oncolytic derivative of the MV Edmonston (MV-Edm) vaccine strain engineered to express the human sodium iodide symporter (NIS; MV-NIS virus). MV-NIS showed significant cytopathic effect (CPE) against prostate cancer cell lines in vitro. Infected cells effectively concentrated radioiodide isotopes as measured in vitro by Iodide-125 ((125)I) uptake assays. Virus localization and spread in vivo could be effectively followed by imaging of (123)I uptake. In vivo administration of MV-NIS either locally or systemically (total dose of 9 x 10(6) TCID(50)) resulted in significant tumor regression (P < 0.05) and prolongation of survival (P < 0.01). Administration of (131)I further enhanced the antitumor effect of MV-NIS virotherapy (P < 0.05). In conclusion, MV-NIS is an oncolytic vector with significant antitumor activity against prostate cancer, which can be further enhanced by (131)I administration. The NIS transgene allows viral localization and monitoring by noninvasive imaging which can facilitate dose optimization in a clinical setting.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Engineered measles virus as a novel oncolytic viral therapy system for hepatocellular carcinoma.Hepatology. 2006 Dec;44(6):1465-77. doi: 10.1002/hep.21437. Hepatology. 2006. PMID: 17133484
-
Engineered measles virus as a novel oncolytic therapy against prostate cancer.Prostate. 2009 Jan 1;69(1):82-91. doi: 10.1002/pros.20857. Prostate. 2009. PMID: 18973133 Free PMC article.
-
Preclinical efficacy of the oncolytic measles virus expressing the sodium iodide symporter in iodine non-avid anaplastic thyroid cancer: a novel therapeutic agent allowing noninvasive imaging and radioiodine therapy.Cancer Gene Ther. 2012 Sep;19(9):659-65. doi: 10.1038/cgt.2012.47. Epub 2012 Jul 13. Cancer Gene Ther. 2012. PMID: 22790962
-
Clinical Trials with Oncolytic Measles Virus: Current Status and Future Prospects.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2018;18(2):177-187. doi: 10.2174/1568009617666170222125035. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2018. PMID: 28228086 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical testing of engineered oncolytic measles virus strains in the treatment of cancer: an overview.Curr Opin Mol Ther. 2009 Feb;11(1):43-53. Curr Opin Mol Ther. 2009. PMID: 19169959 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Intravenous delivery of a multi-mechanistic cancer-targeted oncolytic poxvirus in humans.Nature. 2011 Aug 31;477(7362):99-102. doi: 10.1038/nature10358. Nature. 2011. PMID: 21886163 Clinical Trial.
-
Antibody neutralization of retargeted measles viruses.Virology. 2014 Apr;454-455:237-46. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2014.01.027. Epub 2014 Mar 14. Virology. 2014. PMID: 24725950 Free PMC article.
-
Engineering and combining oncolytic measles virus for cancer therapy.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2020 Dec;56:39-48. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2020.07.005. Epub 2020 Jul 3. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2020. PMID: 32718830 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enhanced noninvasive imaging of oncology models using the NIS reporter gene and bioluminescence imaging.Cancer Gene Ther. 2020 Apr;27(3-4):179-188. doi: 10.1038/s41417-019-0081-2. Epub 2019 Jan 24. Cancer Gene Ther. 2020. PMID: 30674994 Free PMC article.
-
A mechanistic proof-of-concept clinical trial with JX-594, a targeted multi-mechanistic oncolytic poxvirus, in patients with metastatic melanoma.Mol Ther. 2011 Oct;19(10):1913-22. doi: 10.1038/mt.2011.132. Epub 2011 Jul 19. Mol Ther. 2011. PMID: 21772252 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J, Murray T, et al. Cancer statistics, 2008. CA Cancer J Clin. 2008;58:71–96. - PubMed
-
- Griffin DE, Pan CH., and , Moss WJ. Measles vaccines. Front Biosci. 2008;13:1352–1370. - PubMed
-
- Dörig RE, Marcil A, Chopra A., and , Richardson CD. The human CD46 molecule is a receptor for measles virus (Edmonston strain) Cell. 1993;75:295–305. - PubMed
-
- Buettner R, Huang M, Gritsko T, Karras J, Enkemann S, Mesa T, et al. Activated signal transducers and activators of transcription 3 signaling induces CD46 expression and protects human cancer cells from complement-dependent cytotoxicity. Mol Cancer Res. 2007;5:823–832. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

