The interaction of HAb18G/CD147 with integrin alpha6beta1 and its implications for the invasion potential of human hepatoma cells
- PMID: 19775453
- PMCID: PMC2760576
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-9-337
The interaction of HAb18G/CD147 with integrin alpha6beta1 and its implications for the invasion potential of human hepatoma cells
Abstract
Background: HAb18G/CD147 plays pivotal roles in invasion by hepatoma cells, but the underlying mechanism remains unclear. Our previous study demonstrated that overexpression of HAb18G/CD147 promotes invasion by interacting with integrin alpha3beta1. However, it has never been investigated whether alpha3beta1 is solely responsible for this process or if other integrin family members also interact with HAb18G/CD147 in human hepatoma cells.
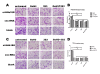
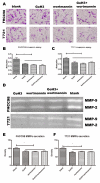
Methods: Human SMMC-7721 and FHCC98 cells were cultured and transfected with siRNA fragments against HAb18G/CD147. The expression levels of HAb18G/CD147 and integrin alpha6beta1 were determined by immunofluorescent double-staining and confocal imaging analysis. Co-immunoprecipitation and Western blot analyses were performed to examine the native conformations of HAb18G/CD147 and integrin alpha6beta1. Invasion potential was evaluated with an invasion assay and gelatin zymography.
Results: We found that integrin alpha6beta1 co-localizes and interacts with HAb18G/CD147 in human hepatoma cells. The enhancing effects of HAb18G/CD147 on invasion capacity and secretion of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) were partially blocked by integrin alpha6beta1 antibodies (P < 0.01). Wortmannin, a specific phosphatidylinositol kinase (PI3K) inhibitor that reverses the effect of HAb18G/CD147 on the regulation of intracellular Ca2+ mobilization, significantly reduced cell invasion potential and secretion of MMPs in human hepatoma cells (P < 0.05). Importantly, no additive effect between Wortmannin and alpha6beta1 antibodies was observed, indicating that alpha6beta1 and PI3K transmit the signal in an upstream-downstream relationship.
Conclusion: These results suggest that alpha6beta1 interacts with HAb18G/CD147 to mediate tumor invasion and metastatic processes through the PI3K pathway.
Figures


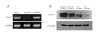


References
-
- Biswas C, Zhang Y, DeCastro R, Guo H, Nakamura T, Kataoka H, Nabeshima K. The human tumor cell-derived collagenase stimulatory factor (renamed EMMPRIN) is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. Cancer Res. 1995;55(2):434–439. - PubMed
-
- Kasinrerk W, Fiebiger E, Stefanova I, Baumruker T, Knapp W, Stockinger H. Human leukocyte activation antigen M6, a member of the Ig superfamily, is the species homologue of rat OX-47, mouse basigin, and chicken HT7 molecule. J Immunol. 1992;149(3):847–854. - PubMed
-
- Miyauchi T, Masuzawa Y, Muramatsu T. The basigin group of the immunoglobulin superfamily: complete conservation of a segment in and around transmembrane domains of human and mouse basigin and chicken HT7 antigen. J Biochem. 1991;110(5):770–774. - PubMed
-
- Chen Z, N YZ, Mi L, Jiang JL, Guo XN. Structure and function analysis of hepatoma associated factor HAb18G. J Cell Mol Immunol. 1999. pp. 34–39.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

