Mutations in the Salmonella enterica serovar Choleraesuis cAMP-receptor protein gene lead to functional defects in the SPI-1 Type III secretion system
- PMID: 19775595
- PMCID: PMC2769549
- DOI: 10.1051/vetres/2009053
Mutations in the Salmonella enterica serovar Choleraesuis cAMP-receptor protein gene lead to functional defects in the SPI-1 Type III secretion system
Abstract
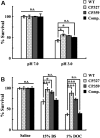
Salmonella enterica serovar Choleraesuis (Salmonella Choleraesuis) causes a lethal systemic infection (salmonellosis) in swine. Live attenuated Salmonella Choleraesuis vaccines are effective in preventing the disease, and isolates of Salmonella Choleraesuis with mutations in the cAMP-receptor protein (CRP) gene (Salmonella Choleraesuis Deltacrp) are the most widely used, although the basis of the attenuation remains unclear. The objective of this study was to determine if the attenuated phenotype of Salmonella Choleraesuis Deltacrp was due to alterations in susceptibility to gastrointestinal factors such as pH and bile salts, ability to colonize or invade the intestine, or cytotoxicity for macrophages. Compared with the parental strain, the survival rate of Salmonella Choleraesuis Deltacrp at low pH or in the presence of bile salts was higher, while the ability of the mutant to invade intestinal epithelia was significantly decreased. In examining the role of CRP on the secretory function of the Salmonella pathogenicity island 1 (SPI-1) encoded type III secretion system (T3SS), it was shown that Salmonella Choleraesuis Deltacrp was unable to secrete the SPI-1 T3SS effector proteins, SopB and SipB, which play a role in Salmonella intestinal invasiveness and macrophage cytotoxicity, respectively. In addition, caspase-1 dependent cytotoxicity for macrophages was significantly reduced in Salmonella Choleraesuis Deltacrp. Collectively, this study demonstrates that the CRP affects the secretory function of SPI-1 T3SS and the resulting ability to invade the host intestinal epithelium, which is a critical element in the pathogenesis of Salmonella Choleraesuis.
Figures


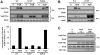

References
-
- Busby S., Ebright R.H., Transcription activation by catabolite activator protein (CAP), J. Mol. Biol. (1999) 293:199–213 - PubMed
-
- Carnell S.C., Bowen A., Morgan E., Maskell D.J., Wallis T.S., Stevens M.P., Role in virulence and protective efficacy in pigs of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium secreted components identified by signature-tagged mutagenesis, Microbiology (2007) 153:1940–1952 - PubMed
-
- Chien M.S., Chan Y.Y., Chen Z.W., Wu C.M., Liao J.W., Chen T.H., et al., Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae serotype 10 derived ApxI induces apoptosis in porcine alveolar macrophages, Vet. Microbiol. (2009) 135:327–333 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
