Crystal structure and functional analysis of homocitrate synthase, an essential enzyme in lysine biosynthesis
- PMID: 19776021
- PMCID: PMC2791007
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.046821
Crystal structure and functional analysis of homocitrate synthase, an essential enzyme in lysine biosynthesis
Abstract
Homocitrate synthase (HCS) catalyzes the first and committed step in lysine biosynthesis in many fungi and certain Archaea and is a potential target for antifungal drugs. Here we report the crystal structure of the HCS apoenzyme from Schizosaccharomyces pombe and two distinct structures of the enzyme in complex with the substrate 2-oxoglutarate (2-OG). The structures reveal that HCS forms an intertwined homodimer stabilized by domain-swapping between the N- and C-terminal domains of each monomer. The N-terminal catalytic domain is composed of a TIM barrel fold in which 2-OG binds via hydrogen bonds and coordination to the active site divalent metal ion, whereas the C-terminal domain is composed of mixed alpha/beta topology. In the structures of the HCS apoenzyme and one of the 2-OG binary complexes, a lid motif from the C-terminal domain occludes the entrance to the active site of the neighboring monomer, whereas in the second 2-OG complex the lid is disordered, suggesting that it regulates substrate access to the active site through its apparent flexibility. Mutations of the active site residues involved in 2-OG binding or implicated in acid-base catalysis impair or abolish activity in vitro and in vivo. Together, these results yield new insights into the structure and catalytic mechanism of HCSs and furnish a platform for developing HCS-selective inhibitors.
Figures


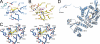


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

