Characterization of GD3 ganglioside as a novel biomarker of mouse neural stem cells
- PMID: 19776077
- PMCID: PMC2782183
- DOI: 10.1093/glycob/cwp149
Characterization of GD3 ganglioside as a novel biomarker of mouse neural stem cells
Abstract
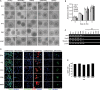
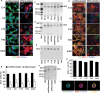
Neural stem cells (NSCs) are undifferentiated neural cells characterized by their high proliferative potential and the capacity for self-renewal with retention of multipotency. Over the past two decades, there has been a huge effort to identify NSCs morphologically, genetically, and molecular biologically. It is still controversial, however, what bona fide NSCs are. To define and characterize NSCs more systematically, it is crucial to explore novel cell-surface marker molecules of NSCs. In this study, we focused on GD3, a b-series ganglioside that is enriched in the immature brain and the subventricular zone (SVZ) of the postnatal and adult brain, and evaluated the usefulness of GD3 as a cell-surface biomarker for identifying NSCs. We demonstrated that GD3 was expressed in more than 80% of NSCs prepared from embryonic, postnatal, and adult mouse brain tissue by the neurosphere culture method. The percentage of GD3-expressing NSCs in neurospheres was nearly the same as it was in neurospheres derived from embryonic, postnatal, and adult brains but decreased drastically to about 40% after differentiation. GD3(+) cells isolated from embryonic mouse striata, postnatal, and adult mouse SVZs by fluorescence-activated cell sorting with an R24 anti-GD3 monoclonal antibody efficiently generated neurospheres compared with GD3(-) cells. These cells possessed multipotency to differentiate into neurons, astrocytes, and oligodendrocytes. These data indicate that GD3 is a unique and powerful cell-surface biomarker to identify and isolate NSCs.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Expression of GD2 and GD3 gangliosides in human embryonic neural stem cells.ASN Neuro. 2011 Apr 7;3(2):e00054. doi: 10.1042/AN20110006. ASN Neuro. 2011. PMID: 21395555 Free PMC article.
-
Ganglioside GD3 regulates neural stem cell quiescence and controls postnatal neurogenesis.Glia. 2024 Jan;72(1):167-183. doi: 10.1002/glia.24468. Epub 2023 Sep 5. Glia. 2024. PMID: 37667994 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of ganglioside GD3 with an EGF receptor sustains the self-renewal ability of mouse neural stem cells in vitro.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Nov 19;110(47):19137-42. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1307224110. Epub 2013 Nov 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 24198336 Free PMC article.
-
Gangliosides in Nerve Cell Specification.Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2018;156:241-263. doi: 10.1016/bs.pmbts.2017.12.008. Epub 2018 Jan 17. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2018. PMID: 29747816 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The culture of neural stem cells.J Cell Biochem. 2009 Jan 1;106(1):1-6. doi: 10.1002/jcb.21972. J Cell Biochem. 2009. PMID: 19021147 Review.
Cited by
-
TNFα-signal and cAMP-mediated signals oppositely regulate melanoma- associated ganglioside GD3 synthase gene in human melanocytes.Sci Rep. 2019 Oct 14;9(1):14740. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-51333-3. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31611597 Free PMC article.
-
GD3 ganglioside is a promising therapeutic target for glioma patients.Neurooncol Adv. 2024 Mar 19;6(1):vdae038. doi: 10.1093/noajnl/vdae038. eCollection 2024 Jan-Dec. Neurooncol Adv. 2024. PMID: 38590763 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Purification, Visualization, and Molecular Signature of Neural Stem Cells.Stem Cells Dev. 2016 Jan 15;25(2):189-201. doi: 10.1089/scd.2015.0190. Epub 2015 Nov 16. Stem Cells Dev. 2016. PMID: 26464067 Free PMC article.
-
Lewis X-carrying N-glycans regulate the proliferation of mouse embryonic neural stem cells via the Notch signaling pathway.J Biol Chem. 2012 Jul 13;287(29):24356-64. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.365643. Epub 2012 May 29. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22645129 Free PMC article.
-
Immunomodulation in stem cell differentiation into neurons and brain repair.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2015 Jun;11(3):474-86. doi: 10.1007/s12015-014-9556-6. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2015. PMID: 25267435 Review.
References
-
- Cammer W, Zhang H. Ganglioside GD3 in radial glia and astrocytes in situ in brains of young and adult mice. J Neurosci Res. 1996;46(1):18–23. - PubMed
-
- Capela A, Temple S. LeX/ssea-1 is expressed by adult mouse CNS stem cells, identifying them as nonependymal. Neuron. 2002;35(5):865–875. - PubMed
-
- Doetsch F, Caille I, Lim DA, Garcia-Verdugo JM, Alvarez-Buylla A. Subventricular zone astrocytes are neural stem cells in the adult mammalian brain. Cell. 1999;97(6):703–716. - PubMed
-
- Gage FH. Mammalian neural stem cells. Science. 2000;287(5457):1433–1438. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

