Motoneuron transplantation rescues the phenotype of SMARD1 (spinal muscular atrophy with respiratory distress type 1)
- PMID: 19776263
- PMCID: PMC6666655
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2734-09.2009
Motoneuron transplantation rescues the phenotype of SMARD1 (spinal muscular atrophy with respiratory distress type 1)
Abstract
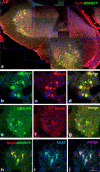
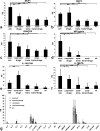
Spinal muscular atrophy with respiratory distress type 1 (SMARD1) is a fatal form of infantile motoneuron disease. There is currently no effective treatment, although motor neuron replacement is a possible therapeutic strategy. We transplanted purified motor neurons into the spinal cord of nmd mice, an animal model of SMARD1. We also administered pharmacological treatment targeting the induction of axonal growth toward skeletal muscle target. At the end stage of the disease, donor-derived motor neurons were detected in the nmd anterior horns, extended axons into the ventral roots, and formed new neuromuscular junctions. These data correlated with improved neuromuscular function and increased life spans. The neuroprotective effect was associated with a reduction in proinflammatory molecules in treated spinal cords. This is the first report that functional restoration of motor units with transplanted motoneurons is feasible in an animal model of a human motoneuron disease, opening up new possibilities for therapeutic intervention.
Figures




References
-
- Arce V, Garces A, de Bovis B, Filippi P, Henderson C, Pettmann B, deLapeyrière O. Cardiotrophin-1 requires LIFRbeta to promote survival of mouse motoneurons purified by a novel technique. J Neurosci Res. 1999;55:119–126. - PubMed
-
- Baron P, Bussini S, Cardin V, Corbo M, Conti G, Galimberti D, Scarpini E, Bresolin N, Wharton SB, Shaw PJ, Silani V. Production of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Muscle Nerve. 2005;32:541–544. - PubMed
-
- Corti S, Locatelli F, Papadimitriou D, Donadoni C, Del Bo R, Fortunato F, Strazzer S, Salani S, Bresolin N, Comi GP. Multipotentiality, homing properties, and pyramidal neurogenesis of CNS-derived LeX(ssea-1)+/CXCR4+ stem cells. FASEB J. 2005;19:1860–1862. - PubMed
-
- Corti S, Locatelli F, Papadimitriou D, Donadoni C, Del Bo R, Crimi M, Bordoni A, Fortunato F, Strazzer S, Menozzi G, Salani S, Bresolin N, Comi GP. Transplanted ALDHhiSSClo neural stem cells generate motor neurons and delay disease progression of nmd mice, an animal model of SMARD1. Hum Mol Genet. 2006;15:167–187. - PubMed
-
- Corti S, Locatelli F, Papadimitriou D, Del Bo R, Nizzardo M, Nardini M, Donadoni C, Salani S, Fortunato F, Strazzer S, Bresolin N, Comi GP. Neural stem cells LewisX+ CXCR4+ modify disease progression in an amyotrophic lateral sclerosis model. Brain. 2007;130:1289–1305. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
