Bioinformatic analyses of transmembrane transport: novel software for deducing protein phylogeny, topology, and evolution
- PMID: 19776645
- PMCID: PMC2814153
- DOI: 10.1159/000239667
Bioinformatic analyses of transmembrane transport: novel software for deducing protein phylogeny, topology, and evolution
Abstract
During the past decade, we have experienced a revolution in the biological sciences resulting from the flux of information generated by genome-sequencing efforts. Our understanding of living organisms, the metabolic processes they catalyze, the genetic systems encoding cellular protein and stable RNA constituents, and the pathological conditions caused by some of these organisms has greatly benefited from the availability of complete genomic sequences and the establishment of comprehensive databases. Many research institutes around the world are now devoting their efforts largely to genome sequencing, data collection and data analysis. In this review, we summarize tools that are in routine use in our laboratory for characterizing transmembrane transport systems. Applications of these tools to specific transporter families are presented. Many of the computational approaches described should be applicable to virtually all classes of proteins and RNA molecules.
Copyright 2009 S. Karger AG, Basel.
Figures
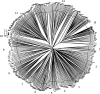
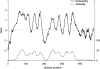
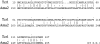
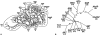
References
-
- Barabote RD, Tamang DG, Abeywardena SN, Fallah NS, Fu JYC, Lio JK, Mirhosseini P, Pezeshk R, Podell S, Salampessy ML, Thever MD, Saier MH., Jr Extra domains in secondary transport carriers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006;1758:1557–1579. - PubMed
-
- Busch W, Saier MH., Jr The IUBMB-Endorsed transporter classification system. Mol Biotech. 2002;27:253–262. - PubMed
-
- Chang AB, Lin R, Keith Studley W, Tran CV, Saier MH., Jr Phylogeny as a guide to structure and function of membrane transport proteins. Mol Membrane Biol. 2004;21:171–181. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

