Sensorimotor network rewiring in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 19777557
- PMCID: PMC6871105
- DOI: 10.1002/hbm.20883
Sensorimotor network rewiring in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
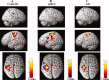
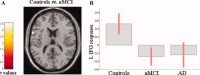
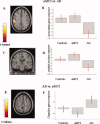
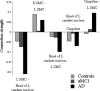
This study aimed at elucidating whether (a) brain areas associated with motor function show a change in functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) signal in amnestic mild cognitive impairment (aMCI) and Alzheimer's disease (AD), (b) such change is linear over the course of the disease, and (c) fMRI changes in aMCI and AD are driven by hippocampal atrophy, or, conversely, reflect a nonspecific neuronal network rewiring generically associated to brain tissue damage. FMRI during the performance of a simple motor task with the dominant right-hand, and structural MRI (i.e., dual-echo, 3D T1-weighted, and diffusion tensor [DT] MRI sequences) were acquired from 10 AD patients, 15 aMCI patients, and 11 healthy controls. During the simple-motor task, aMCI patients had decreased recruitment of the left (L) inferior frontal gyrus compared to controls, while they showed increased recruitment of L postcentral gyrus and head of L caudate nucleus, and decreased activation of the cingulum compared with AD patients. Effective connectivity was altered between primary sensorimotor cortices (SMC) in aMCI patients vs. controls, and between L SMC, head of L caudate nucleus, and cingulum in AD vs. aMCI patients. Altered fMRI activations and connections were correlated with the hippocampal atrophy in aMCI and with the overall GM microstructural damage in AD. Motor-associated functional cortical changes in aMCI and AD mirror fMRI changes of the cognitive network, suggesting the occurrence of a widespread brain rewiring with increasing structural damage rather than a specific response of cognitive network.
Copyright 2009 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Bozzali M, Filippi M, Magnani G, Cercignani M, Franceschi M, Schiatti E, Castiglioni S, Mossini R, Falautano M, Scotti G, Comi G, Falini A ( 2006): The contribution of voxel‐based morphometry in staging patients with mild cognitive impairment. Neurology 67: 453–460. - PubMed
-
- Braak H, Braak E ( 1991): Neuropathological stageing of Alzheimer‐related changes. Acta Neuropathol 82: 239–259. - PubMed
-
- Buckner RL, Snyder AZ, Sanders AL, Raichle ME, Morris JC ( 2000): Functional brain imaging of young, nondemented, and demented older adults. J Cogn Neurosci 12 ( Suppl 2): 24–34. - PubMed
-
- Ceccarelli A, Rocca MA, Falini A, Tortorella P, Pagani E, Rodegher M, Comi G, Scotti G, Filippi M ( 2007): Normal‐appearing white and grey matter damage in MS. A volumetric and diffusion tensor MRI study at 3.0 Tesla. J Neurol 254: 513–518. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

