Repeatability and reproducibility of fetal cardiac ventricular volume calculations using spatiotemporal image correlation and virtual organ computer-aided analysis
- PMID: 19778875
- PMCID: PMC3071609
- DOI: 10.7863/jum.2009.28.10.1301
Repeatability and reproducibility of fetal cardiac ventricular volume calculations using spatiotemporal image correlation and virtual organ computer-aided analysis
Abstract
Objective: The objective of this study was to quantify the repeatability and reproducibility of fetal cardiac ventricular volumes obtained using spatiotemporal image correlation (STIC) and Virtual Organ Computer-Aided Analysis (VOCAL; GE Healthcare, Kretztechnik, Zipf, Austria).
Methods: A technique was developed to compute ventricular volumes using the subfeature Contour Finder: Trace. Twenty-five normal pregnancies were evaluated for the following: (1) to compare the coefficient of variation (CV) of ventricular volumes obtained using 15 degrees and 30 degrees rotation; (2) to compare the CV between 3 methods of quantifying ventricular volumes: (a) Manual Trace, (b) Inversion Mode, and (c) Contour Finder: Trace; and (3) to determine repeatability by calculating agreement and reliability of ventricular volumes when each STIC was measured twice by 3 observers. Reproducibility was assessed by obtaining 2 STICs from each of 44 normal pregnancies. For each STIC, 2 ventricular volume calculations were performed, and agreement and reliability were evaluated. Additionally, measurement error was examined.
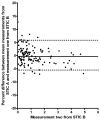
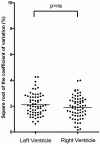
Results: (1) Agreement was better with 15 degrees rotation than 30 degrees (15 degrees: 3.6%; 95% confidence interval [CI], 3.0%-4.2%; versus 30 degrees: 7.1%; 95% CI, 5.8%-8.6%; P < .001); (2) ventricular volumes obtained with Contour Finder: Trace had better agreement than those obtained using either Inversion Mode (Contour Finder: Trace: 3.6%; 95% CI, 3.0%-4.2%; versus Inversion Mode: 6.0%; 95% CI, 4.9%-7.2%; P < .001) or Manual Trace (10.5%; 95% CI, 8.7%-12.5%; P < .001); (3) ventricular volumes were repeatable with good agreement and excellent reliability for both intraobserver and interobserver measurements; and (4) ventricular volumes were reproducible with negligible differences in agreement and good reliability. In addition, bias between STIC acquisitions was minimal (<1%; mean percent difference, -0.4%; 95% limits of agreement, -5.4%-5.9%).
Conclusions: Fetal echocardiography using STIC and VOCAL allows repeatable and reproducible calculation of ventricular volumes with the subfeature Contour Finder: Trace.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of sonographic automatic volume calculation in measuring fetal cardiac ventricular volumes using 4-dimensional sonography: comparison with virtual organ computer-aided analysis.J Ultrasound Med. 2010 Feb;29(2):261-70. doi: 10.7863/jum.2010.29.2.261. J Ultrasound Med. 2010. PMID: 20103798
-
Accuracy, agreement, and reliability of fetal cardiac measurements using 4-dimensional spatiotemporal image correlation.J Ultrasound Med. 2012 Nov;31(11):1719-26. doi: 10.7863/jum.2012.31.11.1719. J Ultrasound Med. 2012. PMID: 23091242
-
Fetal Cardiac Function and Ventricular Volumes Determined by Three-Dimensional Ultrasound Using STIC and VOCAL Methods in Fetuses from Pre-gestational Diabetic Women.Pediatr Cardiol. 2020 Aug;41(6):1125-1134. doi: 10.1007/s00246-020-02362-7. Epub 2020 May 4. Pediatr Cardiol. 2020. PMID: 32367304
-
Fetal cardiac ventricle volumetry in the second half of gestation assessed by 4D ultrasound using STIC combined with inversion mode.Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2007 Aug;30(2):142-51. doi: 10.1002/uog.4036. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2007. PMID: 17566143
-
Fetal heart ventricular mass obtained by STIC acquisition combined with inversion mode and VOCAL.Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2011 Aug;38(2):191-7. doi: 10.1002/uog.8980. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2011. PMID: 21370304
Cited by
-
Evaluation of right ventricular function in fetal hypoplastic left heart syndrome using spatio-temporal image correlation (STIC).Cardiovasc Ultrasound. 2016 Apr 11;14:12. doi: 10.1186/s12947-016-0056-5. Cardiovasc Ultrasound. 2016. PMID: 27066831 Free PMC article.
-
Fetal Intelligent Navigation Echocardiography (FINE): a novel method for rapid, simple, and automatic examination of the fetal heart.Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2013 Sep;42(3):268-84. doi: 10.1002/uog.12563. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2013. PMID: 24000158 Free PMC article.
-
The fetal cardiovascular response to increased placental vascular impedance to flow determined with 4-dimensional ultrasound using spatiotemporal image correlation and virtual organ computer-aided analysis.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2013 Feb;208(2):153.e1-13. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2012.11.043. Epub 2012 Dec 7. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2013. PMID: 23220270 Free PMC article.
-
Fetal cardiac function by three-dimensional ultrasound using 4D-STIC and VOCAL - an update.J Ultrason. 2019 Dec;19(79):287-294. doi: 10.15557/JoU.2019.0043. Epub 2019 Dec 31. J Ultrason. 2019. PMID: 32021711 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ultrasound assessment of fetal cardiac function.Australas J Ultrasound Med. 2013 Nov;16(4):158-167. doi: 10.1002/j.2205-0140.2013.tb00242.x. Epub 2015 Dec 31. Australas J Ultrasound Med. 2013. PMID: 28191192 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Esh-Broder E, Ushakov FB, Imbar T, Yagel S. Application of free-hand three-dimensional echocardiography in the evaluation of fetal cardiac ejection fraction: a preliminary study. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2004;23:546–551. - PubMed
-
- Messing B, Cohen SM, Valsky DV, et al. Fetal cardiac ventricle volumetry in the second half of gestation assessed by 4D ultrasound using STIC combined with inversion mode. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2007;30:142–151. - PubMed
-
- Meyer-Wittkopf M, Cole A, Cooper SG, Schmidt S, Sholler GF. Three-dimensional quantitative echocardiographic assessment of ventricular volume in healthy human fetuses and in fetuses with congenital heart disease. J Ultrasound Med. 2001;20:317–327. - PubMed
-
- Rizzo G, Capponi A, Cavicchioni O, Vendola M, Arduini D. Fetal cardiac stroke volume determination by four-dimensional ultrasound with spatio-temporal image correlation compared with two-dimensional and Doppler ultrasonography. Prenat Diagn. 2007;27:1147–1150. - PubMed
-
- Uittenbogaard LB, Haak MC, Spreeuwenberg MD, Van Vugt JM. Fetal cardiac function assessed with four-dimensional ultrasound imaging using spatiotemporal image correlation. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2009;33:272–281. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

