PKA-dependent phosphorylation of serum response factor inhibits smooth muscle-specific gene expression
- PMID: 19778940
- PMCID: PMC2783385
- DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.109.197285
PKA-dependent phosphorylation of serum response factor inhibits smooth muscle-specific gene expression
Abstract
Objective: Our goal was to identify phosphorylation sites that regulate serum response factor (SRF) activity to gain a better understanding of the signaling mechanisms that regulate SRF's involvement in smooth muscle cell (SMC)-specific and early response gene expression.
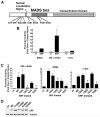
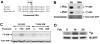
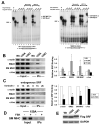
Methods and results: By screening phosphorylation-deficient and mimetic mutations in SRF(-/-) embryonic stem cells, we identified T159 as a phosphorylation site that significantly inhibits SMC-specific gene expression in an embryonic stem cell model of SMC differentiation. This residue conforms to a highly conserved consensus cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA) site, and in vitro and in vivo labeling studies demonstrated that it was phosphorylated by PKA. Results from gel shift and chromatin immunoprecipitation assays demonstrated that T159 phosphorylation inhibited SRF binding to SMC-specific CArG elements. Interestingly, the myocardin factors could at least partially rescue the effects of the T159D mutation under some conditions, but this response was promoter specific. Finally, PKA signaling had much less of an effect on c-fos promoter activity and SRF binding to the c-fos CArG.
Conclusions: Our results indicate that phosphorylation of SRF by PKA inhibits SMC-specific transcription suggesting a novel signaling mechanism for the control of SMC phenotype.
Figures



References
-
- Ross R. The pathogenesis of atherosclerosis: a perspective for the 1990s. Nature. 1993;362:801–9. - PubMed
-
- Owens GK, Kumar MS, Wamhoff BR. Molecular regulation of vascular smooth muscle cell differentiation in development and disease. Physiol Rev. 2004;84:767–801. - PubMed
-
- Mack CP, Owens GK. Regulation of smooth muscle alpha-actin expression in vivo is dependent on CArG elements within the 5′ and first intron promoter regions. Circ Res. 1999;84:852–61. - PubMed
-
- Mack CP, Thompson MM, Lawrenz-Smith S, Owens GK. Smooth muscle alpha-actin CArG elements coordinate formation of a smooth muscle cell-selective, serum response factor-containing activation complex. Circ Res. 2000;86:221–32. - PubMed
-
- Madsen CS, Hershey JC, Hautmann MB, White SL, Owens GK. Expression of the smooth muscle myosin heavy chain gene is regulated by a negative-acting GC-rich element located between two positive-acting serum response factor-binding elements. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:6332–40. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

