TLR3-mediated NF-{kappa}B signaling in human esophageal epithelial cells
- PMID: 19779021
- PMCID: PMC2850089
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00065.2009
TLR3-mediated NF-{kappa}B signaling in human esophageal epithelial cells
Abstract
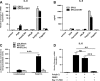
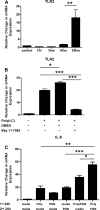
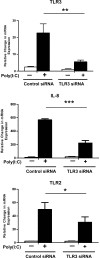
Despite its position at the front line against ingested pathogens, very little is presently known about the role of the esophageal epithelium in host innate immune defense. As a key player in the innate immune response, Toll-like receptor (TLR) signaling has not been well characterized in human esophageal epithelial cells. In the present study, we investigated the inflammatory response and signaling pathways activated by TLR stimulation of human esophageal cells in vitro. Using quantitative RT-PCR, we profiled the expression pattern of human TLRs 1-10 in primary esophageal keratinocytes (EPC2), immortalized nontransformed esophageal keratinocytes (EPC2-hTERT), and normal human esophageal mucosal biopsies and found that TLRs 1, 2, 3, and 5 were expressed both in vivo and in vitro. Using the cytokine IL-8 as a physiological read out of the inflammatory response, we found that TLR3 is the most functional of the expressed TLRs in both primary and immortalized esophageal epithelial cell lines in response to its synthetic ligand polyinosinic polycytidylic acid [poly(I:C)]. Through reporter gene studies, we show that poly(I:C)-induced NF-kappaB activation is critical for the transactivation of the IL-8 promoter in vitro and that nuclear translocation of NF-kappaB occurs at an early time point following poly(I:C) stimulation of esophageal epithelial cells. Importantly, we also show that poly(I:C) stimulation induces the NF-kappaB-dependent esophageal epithelial expression of TLR2, leading to enhanced epithelial responsiveness of EPC2-hTERT cells to TLR2 ligand stimulation, suggesting an important regulatory role for TLR3-mediated NF-kappaB signaling in the innate immune response of esophageal epithelial cells. Our findings demonstrate for the first time that TLR3 is highly functional in the human esophageal epithelium and that TLR3-mediated NF-kappaB signaling may play an important regulatory role in esophageal epithelial homeostasis.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Various members of the Toll-like receptor family contribute to the innate immune response of human epidermal keratinocytes.Immunology. 2005 Apr;114(4):531-41. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2005.02122.x. Immunology. 2005. PMID: 15804290 Free PMC article.
-
Toll-like receptor agonists induce inflammation and cell death in a model of head and neck squamous cell carcinomas.Immunology. 2009 Sep;128(1 Suppl):e600-11. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2008.03041.x. Epub 2008 Dec 26. Immunology. 2009. PMID: 19740321 Free PMC article.
-
Toll-like receptor 3 signaling enables human esophageal epithelial cells to sense endogenous danger signals released by necrotic cells.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2011 Jul;301(1):G91-9. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00471.2010. Epub 2011 Apr 7. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21474651 Free PMC article.
-
A Comprehensive Review of poly(I: C) as a Tool for Investigating Astrocytic TLR3 Signaling.Neurochem Res. 2025 Apr 2;50(2):133. doi: 10.1007/s11064-025-04381-3. Neurochem Res. 2025. PMID: 40172723 Review.
-
Pre- and post-conditioning with poly I:C exerts neuroprotective effect against cerebral ischemia injury in animal models: A systematic review and meta-analysis.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2022 Aug;28(8):1168-1182. doi: 10.1111/cns.13851. Epub 2022 May 5. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2022. PMID: 35510663 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Eosinophilic Esophagitis: A Comprehensive Review.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2016 Apr;50(2):159-74. doi: 10.1007/s12016-015-8501-z. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26194940 Review.
-
Whole cigarette smoke increased the expression of TLRs, HBDs, and proinflammory cytokines by human gingival epithelial cells through different signaling pathways.PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e52614. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0052614. Epub 2012 Dec 28. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23300722 Free PMC article.
-
Type 2 Inflammation in Eosinophilic Esophagitis: From Pathophysiology to Therapeutic Targets.Front Physiol. 2022 Jan 12;12:815842. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.815842. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35095572 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human esophageal myofibroblasts secrete proinflammatory cytokines in response to acid and Toll-like receptor 4 ligands.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2015 Jun 1;308(11):G904-23. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00333.2014. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25882613 Free PMC article.
-
The immune-epithelial interface in eosinophilic esophagitis: a conversation.Front Allergy. 2023 Oct 3;4:1270581. doi: 10.3389/falgy.2023.1270581. eCollection 2023. Front Allergy. 2023. PMID: 37854541 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Abraham E, Arcaroli J, Carmody A, Wang H, Tracey K. Cutting edge: HMG-1 as a mediator of acute lung inflammation. J Immunol 165: 2950–2954, 2000 - PubMed
-
- Abreu MT, Vora P, Faure E, Thomas LS, Arnold ET, Arditi M. Decreased expression of Toll-like receptor-4 and MD-2 correlates with intestinal epithelial cell protection against dysregulated proinflammatory gene expression in response to bacterial lipopolysaccharide. J Immunol 167: 1609–1616, 2001 - PubMed
-
- Alexander JA, Brouillette DE, Chien MC, Yoo YK, Tarter RE, Gavaler JS, Van Thiel DH. Infectious esophagitis following liver and renal transplantation. Dig Dis Sci 33: 1121–1126, 1988 - PubMed
-
- Alexopoulou L, Holt AC, Medzhitov R, Flavell RA. Recognition of double-stranded RNA and activation of NF-kappaB by Toll-like receptor 3. Nature 413: 732–738, 2001 - PubMed
-
- An H, Xu H, Yu Y, Zhang M, Qi R, Yan X, Liu S, Wang W, Guo Z, Qin Z, Cao X. Up-regulation of TLR9 gene expression by LPS in mouse macrophages via activation of NF-kappaB, ERK and p38 MAPK signal pathways. Immunol Lett 81: 165–169, 2002 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

