Serum LH correlates highly with intratesticular steroid levels in normal men
- PMID: 19779211
- PMCID: PMC2866133
- DOI: 10.2164/jandrol.109.008391
Serum LH correlates highly with intratesticular steroid levels in normal men
Abstract
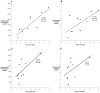
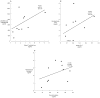
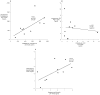
Sex steroids are essential for spermatogenesis; however, normal intratesticular concentrations of these hormones in man have not been extensively studied. To improve our understanding of intratesticular hormone concentrations, we performed bilateral testicular aspirations in a group of normal men, determined sex steroid concentrations within each testis, and compared these levels to serum hormone concentrations. Ten healthy human subjects aged 20-49 underwent bilateral testicular aspirations. Intratesticular hormone concentrations of testosterone, dihydrotestosterone (DHT), and estradiol were measured using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Intratesticular testosterone concentrations ranged from 119 to 1251 ng/mL, with a mean of 635 +/- 368 ng/mL. Intratesticular estradiol ranged from 0.41 to 3.9 ng/mL, with a mean of 2.4 +/- 1.3 ng/mL. Intratesticular DHT ranged from 1.1 to 7.9 ng/mL, with a mean of 3.5 +/- 3.2 ng/mL. Intratesticular testosterone and estradiol concentrations correlated highly with serum luteinizing hormone (LH; r = 0.87 and r = 0.70 respectively, P < .01). Intratesticular testosterone correlated highly with serum testosterone. Moreover, a significant correlation between the right and left testes was observed for testosterone (r = 0.82, P = .003), but not for estradiol or DHT. Intratesticular hormone concentrations can be safely assessed by testicular aspiration. Intratesticular testosterone and estradiol correlate highly with serum LH concentrations, and variation in serum LH accounts for most of the variation in intratesticular testosterone among men. In addition, intratesticular testosterone is highly correlated between testes in a given individual. Direct measurement of intratesticular testosterone will improve our understanding of the relationship between intratesticular sex steroids and spermatogenesis, and may have implications for the development of male hormonal contraception.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Studies of the human testis. XVII. Gonadotropin regulation of intratesticular testosterone and estradiol in infertile men.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1982 Dec;55(6):1073-80. doi: 10.1210/jcem-55-6-1073. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1982. PMID: 6813345
-
Serum luteinizing hormone pulsatility and intratesticular testosterone and oestradiol concentrations in idiopathic infertile men with high and normal follicle stimulating hormone serum concentrations.Hum Reprod. 1994 May;9(5):781-7. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.humrep.a138596. Hum Reprod. 1994. PMID: 7929722
-
The content of five sex steroids in human testis.Physiol Res. 2012;61(2):221-5. doi: 10.33549/physiolres.932156. Epub 2012 Jan 31. Physiol Res. 2012. PMID: 22292719
-
Physiologic role and regulation of intratesticular sex steroids.Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2011 Jun;18(3):217-23. doi: 10.1097/MED.0b013e328345d50e. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2011. PMID: 21478750 Review.
-
The influence of pharmaceutical compounds on male fertility.Andrologia. 1976;8(3):203-35. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0272.1976.tb02137.x. Andrologia. 1976. PMID: 793446 Review.
Cited by
-
Serum insulin-like factor 3 is highly correlated with intratesticular testosterone in normal men with acute, experimental gonadotropin deficiency stimulated with low-dose human chorionic gonadotropin: a randomized, controlled trial.Fertil Steril. 2013 Jan;99(1):132-139. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2012.09.009. Epub 2012 Oct 3. Fertil Steril. 2013. PMID: 23040523 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Anabolic-Androgenic Steroid Misuse: Mechanisms, Patterns of Misuse, User Typology, and Adverse Effects.J Sports Med (Hindawi Publ Corp). 2021 Dec 10;2021:7497346. doi: 10.1155/2021/7497346. eCollection 2021. J Sports Med (Hindawi Publ Corp). 2021. PMID: 34926695 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Roles of Luteinizing Hormone, Follicle-Stimulating Hormone and Testosterone in Spermatogenesis and Folliculogenesis Revisited.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 25;22(23):12735. doi: 10.3390/ijms222312735. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34884539 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Determination of Intraprostatic and Intratesticular Androgens.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 5;22(1):466. doi: 10.3390/ijms22010466. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33466491 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Follicle-stimulating Hormone (FSH) Action on Spermatogenesis: A Focus on Physiological and Therapeutic Roles.J Clin Med. 2020 Apr 3;9(4):1014. doi: 10.3390/jcm9041014. J Clin Med. 2020. PMID: 32260182 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ahmad N, Haltmeyer GC, Eik-Nes KB. Maintenance of spermatogenesis in rats with intratesticular implants containing testosterone or dihydrotestosterone (DHT) Biol Reprod. 1973;8:411–419. - PubMed
-
- Amory JK, Page ST, Bremner WJ. Oral testosterone in oil: pharmacokinetic effects of 5alpha reduction by finasteride or dutasteride and food intake in men. J Androl. 2006;27:72–78. - PubMed
-
- Amory JK, Wang C, Swerdloff RS, Anawalt BD, Matsumoto AM, Bremner WJ, Walker SE, Haberer LJ, Clark RV. The effect of 5alpha-reductase inhibition with dutasteride and finasteride on semen parameters and serum hormones in healthy men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007;92:1659–1665. - PubMed
-
- Anderson RA, Wallace AM, Wu FC. Comparison between testosterone enanthate-induced azoospermia and oligozoospermia in a male contraceptive study. III. Higher 5 alpha-reductase activity in oligozoospermic men administered supraphysiological doses of testosterone. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1996;81:902–908. - PubMed
-
- Baker HW, Santen RJ, Burger HG, De Kretser DM, Hudson B, Pepperell RJ, Bardin CW. Rhythms in the secretion of gonadotropins and gonadal steroids. J Steroid Biochem. 1975;6:793–801. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

