RNase Y, a novel endoribonuclease, initiates riboswitch turnover in Bacillus subtilis
- PMID: 19779461
- PMCID: PMC2782095
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2009.283
RNase Y, a novel endoribonuclease, initiates riboswitch turnover in Bacillus subtilis
Abstract
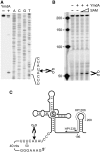
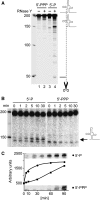
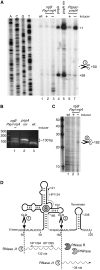
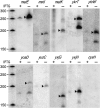
In contrast to Escherichia coli, initiation of mRNA decay in Gram-positive organisms is poorly understood. We studied the fate of the highly structured RNAs generated by premature transcription termination of S-adenosylmethionine (SAM)-dependent riboswitches in Bacillus subtilis. An essential protein of earlier unknown function, YmdA, was identified as a novel endoribonuclease (now called RNase Y) that was capable of preferential cleaving in vitro of the 5' monophosphorylated yitJ riboswitch upstream of the SAM-binding aptamer domain. Antiterminated full-length yitJ mRNA was not a substrate for RNase Y in vivo and in vitro, transcripts capable of forming the antiterminator were only cleaved in the presence of SAM. Turnover of 10 other SAM-dependent riboswitches was also initiated by RNase Y. Depletion of this ribonuclease increased the half-life of bulk mRNA more than two-fold. This indicates that RNase Y might be not only important for riboswitch RNA turnover but also as a key player in the initiation of mRNA decay in B. subtilis. About 40% of the sequenced eubacterial species have an RNase Y orthologue.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Aravind L, Koonin EV (1998) The HD domain defines a new superfamily of metal-dependent phosphohydrolases. Trends Biochem Sci 23: 469–472 - PubMed
-
- Callaghan AJ, Marcaida MJ, Stead JA, McDowall KJ, Scott WG, Luisi BF (2005) Structure of Escherichia coli RNase E catalytic domain and implications for RNA turnover. Nature 437: 1187–1191 - PubMed
-
- Carpousis AJ, Luisi BF, McDowall KJ (2009) Endonucleolytic initiation of mRNA decay in Escherichia coli. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol 85: 91–135 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

