Independent slab-phase modulation combined with parallel imaging in bilateral breast MRI
- PMID: 19780156
- PMCID: PMC4105446
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.22115
Independent slab-phase modulation combined with parallel imaging in bilateral breast MRI
Abstract
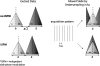
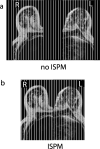
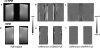
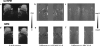
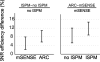
Independent slab-phase modulation allows three-dimensional imaging of multiple volumes without encoding the space between volumes, thus reducing scan time. Parallel imaging further accelerates data acquisition by exploiting coil sensitivity differences between volumes. This work compared bilateral breast image quality from self-calibrated parallel imaging reconstruction methods such as modified sensitivity encoding, generalized autocalibrating partially parallel acquisitions and autocalibrated reconstruction for Cartesian sampling (ARC) for data with and without slab-phase modulation. A study showed an improvement of image quality by incorporating slab-phase modulation. Geometry factors measured from phantom images were more homogenous and lower on average when slab-phase modulation was used for both mSENSE and GRAPPA reconstructions. The resulting improved signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) was validated for in vivo images as well using ARC instead of GRAPPA, illustrating average SNR efficiency increases in mSENSE by 5% and ARC by 8% based on region of interest analysis. Furthermore, aliasing artifacts from mSENSE reconstruction were reduced when slab-phase modulation was used. Overall, slab-phase modulation with parallel imaging improved image quality and efficiency for 3D bilateral breast imaging.
(c) 2009 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures





References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J, Murray T, Thun MJ. Cancer statistics, 2008. CA Cancer J Clin. 2008;58:71–96. - PubMed
-
- Berry DA, Cronin KA, Plevritis SK, Fryback DG, Clarke L, Zelen M, Mandelblatt JS, Yakovlev AY, Habbema JD, Feuer EJ. Effect of screening and adjuvant therapy on mortality from breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:1784–1792. - PubMed
-
- Kolb TM, Lichy J, Newhouse JH. Comparison of the performance of screening mammography, physical examination, and breast US and evaluation of factors that influence them: an analysis of 27,825 patient evaluations. Radiology. 2002;225:165–175. - PubMed
-
- Kriege M, Brekelmans CT, Boetes C, Besnard PE, Zonderland HM, Obdeijn IM, Manoliu RA, Kok T, Peterse H, Tilanus-Linthorst MM, Muller SH, Meijer S, Oosterwijk JC, Beex LV, Tollenaar RA, de Koning HJ, Rutgers EJ, Klijn JG. Efficacy of MRI and mammography for breast-cancer screening in women with a familial or genetic predisposition. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:427–437. - PubMed
-
- Leach MO, Boggis CR, Dixon AK, Easton DF, Eeles RA, Evans DG, Gilbert FJ, Griebsch I, Ho RJ, Kessar P, Lakhani SR, Moss SM, Nerurkar A, Padhani AR, Pointon LJ, Thompson D, Warren RM. Screening with magnetic resonance imaging and mammography of a UK population at high familial risk of breast cancer: a prospective multicentre cohort study (MARIBS). Lancet. 2005;365:1769–1778. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

