The membrane cytoskeletal protein adducin is phosphorylated by protein kinase C in D1 neurons of the nucleus accumbens and dorsal striatum following cocaine administration
- PMID: 19780900
- PMCID: PMC2810345
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2009.06405.x
The membrane cytoskeletal protein adducin is phosphorylated by protein kinase C in D1 neurons of the nucleus accumbens and dorsal striatum following cocaine administration
Abstract
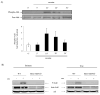
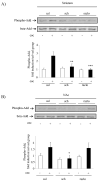
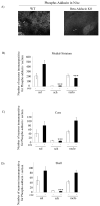
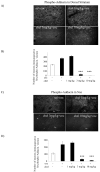
Repeated cocaine administration results in persistent changes in synaptic function in the mesolimbic dopamine system that are thought to be critical for the transition to addiction. Cytoskeletal rearrangement and actin dynamics are essential for this drug-dependent plasticity. Cocaine administration increases levels of F-actin in the nucleus accumbens and is associated with changes in the phosphorylation state of actin-binding proteins. The adducins constitute a family of proteins that interact with actin and spectrin to maintain cellular architecture. The interaction of adducin with these cytoskeletal proteins is regulated by phosphorylation, and it is therefore expected that phosphorylation of adducin may be involved in morphological changes underlying synaptic responses to drugs of abuse including cocaine. In the current study, we characterized the regulation of adducin phosphorylation in the nucleus accumbens and dorsal striatum in response to various regimen of cocaine. Our results demonstrate that adducin is phosphorylated by protein kinase C in medium spiny neurons that express the dopamine D1 receptor. These data indicate that adducin phosphorylation is a signaling event regulated by cocaine administration and further suggest that adducin may be involved in remodeling of the neuronal cytoskeleton in response to cocaine administration.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Opposing patterns of signaling activation in dopamine D1 and D2 receptor-expressing striatal neurons in response to cocaine and haloperidol.J Neurosci. 2008 May 28;28(22):5671-85. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1039-08.2008. J Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 18509028 Free PMC article.
-
Whole-cell plasticity in cocaine withdrawal: reduced sodium currents in nucleus accumbens neurons.J Neurosci. 1998 Jan 1;18(1):488-98. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-01-00488.1998. J Neurosci. 1998. PMID: 9412525 Free PMC article.
-
Essential role of D1R in the regulation of mTOR complex1 signaling induced by cocaine.Neuropharmacology. 2015 Dec;99:610-9. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2015.08.024. Epub 2015 Aug 24. Neuropharmacology. 2015. PMID: 26314207 Free PMC article.
-
Acute binge pattern cocaine administration induces region-specific effects in D1-r- and D2-r-expressing cells in eGFP transgenic mice.Neuroscience. 2013 Dec 3;253:123-31. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.08.032. Epub 2013 Aug 31. Neuroscience. 2013. PMID: 24001687
-
Cocaine-seeking is associated with PKC-dependent reduction of excitatory signaling in accumbens shell D2 dopamine receptor-expressing neurons.Neuropharmacology. 2015 May;92:80-9. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2015.01.002. Epub 2015 Jan 14. Neuropharmacology. 2015. PMID: 25596492 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
γ-Adducin promotes process outgrowth and secretory protein exit from the Golgi apparatus.J Mol Neurosci. 2013 Jan;49(1):1-10. doi: 10.1007/s12031-012-9827-0. Epub 2012 Jun 17. J Mol Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 22706708 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-145 functions as a tumor-suppressive RNA by targeting Sox9 and adducin 3 in human glioma cells.Neuro Oncol. 2013 Oct;15(10):1302-16. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/not090. Epub 2013 Jun 28. Neuro Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23814265 Free PMC article.
-
DARPP-32 interaction with adducin may mediate rapid environmental effects on striatal neurons.Nat Commun. 2015 Dec 7;6:10099. doi: 10.1038/ncomms10099. Nat Commun. 2015. PMID: 26639316 Free PMC article.
-
Constitutive knockout of the membrane cytoskeleton protein beta adducin decreases mushroom spine density in the nucleus accumbens but does not prevent spine remodeling in response to cocaine.Eur J Neurosci. 2013 Jan;37(1):1-9. doi: 10.1111/ejn.12037. Epub 2012 Oct 29. Eur J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23106536 Free PMC article.
-
Methylphenidate exerts dose-dependent effects on glutamate receptors and behaviors.Biol Psychiatry. 2014 Dec 15;76(12):953-62. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2014.04.003. Epub 2014 Apr 12. Biol Psychiatry. 2014. PMID: 24832867 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aujla H, Beninger RJ. Intra-accumbens protein kinase C inhibitor NPC 15437 blocks amphetamine-produced conditioned place preference in rats. Behavioural brain research. 2003;147:41–48. - PubMed
-
- Chen CL, Hsieh YT, Chen HC. Phosphorylation of adducin by protein kinase Cdelta promotes cell motility. Journal of cell science. 2007;120:1157–1167. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

