BK Channels: mediators and models for alcohol tolerance
- PMID: 19781792
- PMCID: PMC4115799
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tins.2009.08.001
BK Channels: mediators and models for alcohol tolerance
Abstract
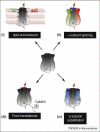
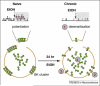
Enhanced acute tolerance predicts alcohol abuse. We describe work on the role of the calcium- and voltage-gated BK channel in alcohol tolerance, highlighting the lipid environment, BK protein isoform selection and auxiliary BK channel proteins. We show how ethanol, which had the reputation of a nonspecific membrane perturbant, is now being examined at realistic concentrations with cutting-edge techniques, providing novel molecular targets for therapeutic approaches to alcoholism. Addictive disorders impact our emotional, physical and financial status, and burden our healthcare system. Although alcohol is the focus of this review, it is highly probable, given the common neural and biochemical pathways used by drugs of abuse, that the findings described here will also apply to other drugs.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Alcohol tolerance in large-conductance, calcium-activated potassium channels of CNS terminals is intrinsic and includes two components: decreased ethanol potentiation and decreased channel density.J Neurosci. 2004 Sep 22;24(38):8322-32. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1536-04.2004. J Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15385615 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a BK channel auxiliary protein controlling molecular and behavioral tolerance to alcohol.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Nov 11;105(45):17543-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0801068105. Epub 2008 Nov 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 18981408 Free PMC article.
-
Ethanol's interaction with BK channel α subunit residue K361 does not mediate behavioral responses to alcohol in mice.Mol Psychiatry. 2024 Feb;29(2):529-542. doi: 10.1038/s41380-023-02346-y. Epub 2023 Dec 22. Mol Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 38135755 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of BK Channels by Ethanol.Int Rev Neurobiol. 2016;128:239-79. doi: 10.1016/bs.irn.2016.03.019. Epub 2016 May 12. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2016. PMID: 27238266 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Voltage-Sensitive Potassium Channels of the BK Type and Their Coding Genes Are Alcohol Targets in Neurons.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2018;248:281-309. doi: 10.1007/164_2017_78. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29204711 Review.
Cited by
-
Ethanol modulation of mammalian BK channels in excitable tissues: molecular targets and their possible contribution to alcohol-induced altered behavior.Front Physiol. 2014 Dec 2;5:466. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2014.00466. eCollection 2014. Front Physiol. 2014. PMID: 25538625 Free PMC article. Review.
-
KCNQ channels show conserved ethanol block and function in ethanol behaviour.PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e50279. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0050279. Epub 2012 Nov 29. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23209695 Free PMC article.
-
The Emerging Role of Non-Coding RNAs in Drug Addiction.Front Genet. 2012 Jun 22;3:106. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2012.00106. eCollection 2012. Front Genet. 2012. PMID: 22737160 Free PMC article.
-
Signaling pathways mediating alcohol effects.Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2013;13:87-126. doi: 10.1007/7854_2011_161. Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 21877259 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neurobiological signatures of alcohol dependence revealed by protein profiling.PLoS One. 2013 Dec 16;8(12):e82656. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0082656. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24358215 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kalant H. Research on tolerance: what can we learn from history? Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 1998;22:67–76. - PubMed
-
- Schuckit MA. Low level of response to alcohol as a predictor of future alcoholism. Am. J. Psychiatry. 1994;151:184–189. - PubMed
-
- Brodie MS, et al. Ethanol interactions with calcium-dependent potassium channels. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 2007;31:1625–1632. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

