Modulation of hepatic fibrosis by c-Jun-N-terminal kinase inhibition
- PMID: 19782079
- PMCID: PMC2988578
- DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2009.09.015
Modulation of hepatic fibrosis by c-Jun-N-terminal kinase inhibition
Abstract
Background & aims: c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) is activated by multiple profibrogenic mediators; JNK activation occurs during toxic, metabolic, and autoimmune liver injury. However, its role in hepatic fibrogenesis is unknown.
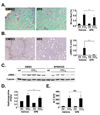
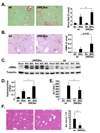
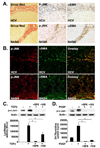
Methods: JNK phosphorylation was detected by immunoblot analysis and confocal immunofluorescent microscopy in fibrotic livers from mice after bile duct ligation (BDL) or CCl(4) administration and in liver samples from patients with chronic hepatitis C and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Fibrogenesis was investigated in mice given the JNK inhibitor SP600125 and in JNK1- and JNK2-deficient mice following BDL or CCl(4) administration. Hepatic stellate cell (HSC) activation was determined in primary mouse HSCs incubated with pan-JNK inhibitors SP600125 and VIII.
Results: JNK phosphorylation was strongly increased in livers of mice following BDL or CCl(4) administration as well as in human fibrotic livers, occurring predominantly in myofibroblasts. In vitro, pan-JNK inhibitors prevented transforming growth factor (TGF) beta-, platelet-derived growth factor-, and angiotensin II-induced murine HSC activation and decreased platelet-derived growth factor and TGF-beta signaling in human HSCs. In vivo, pan-JNK inhibition did not affect liver injury but significantly reduced fibrosis after BDL or CCl(4). JNK1-deficient mice had decreased fibrosis after BDL or CCl(4), whereas JNK2-deficient mice displayed increased fibrosis after BDL but fibrosis was not changed after CCl(4). Moreover, patients with chronic hepatitis C who displayed decreased fibrosis in response to the angiotensin receptor type 1 blocker losartan showed decreased JNK phosphorylation.
Conclusions: JNK is involved in HSC activation and fibrogenesis and represents a potential target for antifibrotic treatment approaches.
Copyright 2010 AGA Institute. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures: No conflicting interests exist.
Figures




References
-
- Minden A, Karin M. Regulation and function of the JNK subgroup of MAP kinases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1997;1333:F85–F104. - PubMed
-
- Weston CR, Davis RJ. The JNK signal transduction pathway. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2007;19:142–149. - PubMed
-
- Hibi M, Lin A, Smeal T, Minden A, Karin M. Identification of an oncoprotein- and UV-responsive protein kinase that binds and potentiates the c-Jun activation domain. Genes Dev. 1993;7:2135–2148. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

