Protection against nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae challenges by mucosal vaccination with a detoxified lipooligosaccharide conjugate in two chinchilla models
- PMID: 19782149
- PMCID: PMC2818210
- DOI: 10.1016/j.micinf.2009.09.006
Protection against nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae challenges by mucosal vaccination with a detoxified lipooligosaccharide conjugate in two chinchilla models
Abstract
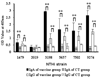
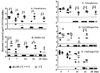
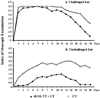
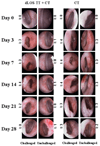
Otitis media (OM) can occur following outset of upper respiratory tract infections. Inhibition of bacterial colonization in nasopharynx (NP) by mucosal vaccination may prevent OM by reducing bacterial invasion of the middle ears (MEs). In this study, 80 chinchillas were intranasally (i.n.) immunized with a detoxified lipooligosaccharide (dLOS)-tetanus toxoid conjugate vaccine of nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae (NTHi) mixed with cholera toxin (CT) or CT alone. All vaccinated animals responded with elevated levels of mucosal and serum anti-LOS antibodies. Two weeks after the last immunization, 40 chinchillas were challenged i.n. with NTHi to evaluate NP colonization and ME infection while the rest of the animals were challenged transbullarly (T.B.) to examine the development of OM. Compared to the control group, the vaccination inhibited not only bacterial colonization in NP and transmission to MEs in the i.n. challenge group but also bacterial colonization in NP and transmission to unchallenged ears in the T.B. challenge group. Though no difference was found in the challenged ears of either group right after the T.B. challenge, an early clearance of NTHi from NP and unchallenged ears as well as less severity of OM in the unchallenged ears were observed in vaccinated animals. Current results along with our previous data indicate that mucosal vaccination is capable of inhibiting NTHi NP colonization and preventing OM occurrence in chinchillas; the i.n. challenge model is preferable for testing the mucosal vaccines while the T.B. challenge model is superior for testing the systemic vaccines.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Intranasal immunization with a lipooligosaccharide-based conjugate vaccine from nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae enhances bacterial clearance in mouse nasopharynx.FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2003 Jan 21;35(1):1-10. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-695X.2003.tb00642.x. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 12589951
-
Detoxified lipooligosaccharide from nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae conjugated to proteins confers protection against otitis media in chinchillas.Infect Immun. 1997 Nov;65(11):4488-93. doi: 10.1128/iai.65.11.4488-4493.1997. Infect Immun. 1997. PMID: 9353024 Free PMC article.
-
Immunogenicity of Nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae Outer Membrane Vesicles and Protective Ability in the Chinchilla Model of Otitis Media.Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2017 Oct 5;24(10):e00138-17. doi: 10.1128/CVI.00138-17. Print 2017 Oct. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28768669 Free PMC article.
-
Developing a vaccine to prevent otitis media caused by nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae.Expert Rev Vaccines. 2016 Jul;15(7):863-78. doi: 10.1586/14760584.2016.1156539. Epub 2016 Mar 17. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2016. PMID: 26894630 Review.
-
Developing a nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae (NTHi) vaccine.Vaccine. 2000 Dec 8;19 Suppl 1:S108-15. doi: 10.1016/s0264-410x(00)00288-7. Vaccine. 2000. PMID: 11163473 Review.
Cited by
-
Cigarette smoke exposure exacerbates lung inflammation and compromises immunity to bacterial infection.J Immunol. 2014 Jun 1;192(11):5226-35. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1302584. Epub 2014 Apr 21. J Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24752444 Free PMC article.
-
Genome sequencing of disease and carriage isolates of nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae identifies discrete population structure.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Apr 8;111(14):5439-44. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1403353111. Epub 2014 Mar 25. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 24706866 Free PMC article.
-
Intranasal immunization with nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae outer membrane vesicles induces cross-protective immunity in mice.PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e42664. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0042664. Epub 2012 Aug 3. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22880074 Free PMC article.
-
Phase variable acetylation of lipooligosaccharide modifies antibody production and opsonophagocytic killing of non-typeable Haemophilus influenzae.iScience. 2023 Aug 30;26(10):107785. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.107785. eCollection 2023 Oct 20. iScience. 2023. PMID: 37727736 Free PMC article.
-
Shielding of a lipooligosaccharide IgM epitope allows evasion of neutrophil-mediated killing of an invasive strain of nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae.mBio. 2014 Jul 22;5(4):e01478-14. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01478-14. mBio. 2014. PMID: 25053788 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bondy J, Berman S, Glazner J, Lezotte D. Direct expenditures related to otitis media diagnosis: extrapolations from a pediatric Medicaid cohort. Pediatrics. 2000;105:e72. - PubMed
-
- Benninger M. Acute bacterial rhinosinusitis and otitis media: changes in pathogenicity following widespread use of pneumococcal conjugate vaccine. Otolaryngol. Head Neck. Surg. 2008;138:274–278. - PubMed
-
- Casey J, Pichichero M. Changes in frequency and pathogens causing acute otitis media in 1995–2003. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2004;23:824–828. - PubMed
-
- Prymula R, Peeters P, Chrobok V, Kriz P, Novakova E, Kaliskova E, Kohl I, Lommel P, Poolman J, Prieels J, Schuerman L. Pneumococcal capsular polysaccharides conjugated to protein D for prevention of acute otitis media caused by both Streptococcus pneumoniae and non-typable Haemophilus influenzae: a randomized double-blind efficacy study. Lancet. 2006;367:740–748. - PubMed
-
- Hanage W, Huang S, Lipsitch M, Bishop C, Godoy D, Pelton S, Goldstein R, Huot H, Finkelstein J. Diversity and antibiotic resistance among nonvaccine serotypes of Streptococcus pneumoniae carriage isolates in the post-heptavalent conjugate vaccine era. J. Infect. Dis. 2007;195:347–352. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

