Baseline differences in the HF-ACTION trial by sex
- PMID: 19782784
- PMCID: PMC3748941
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ahj.2009.07.012
Baseline differences in the HF-ACTION trial by sex
Abstract
Background: In patients with heart failure (HF), assessment of functional capacity plays an important prognostic role. Both 6-minute walk and cardiopulmonary exercise testing have been used to determine physical function and to determine prognosis and even listing for transplantation. However, as in HF trials, the number of women reported has been small, and the cutoffs for transplantation have been representative of male populations and extrapolated to women. It is also well known that peak VO(2) as a determinant of fitness is inherently lower in women than in men and potentially much lower in the presence of HF. Values for a female population from which to draw for this important determination are lacking.
Methods: The HF-ACTION trial randomized 2,331 patients (28% women) with New York Heart Association class II-IV HF due to systolic dysfunction to either a formal exercise program in addition to optimal medical therapy or to optimal medical therapy alone without any formal exercise training. To characterize differences between men and women in the interpretation of final cardiopulmonary exercise testing models, the interaction of individual covariates with sex was investigated in the models of (1) VE/VCO(2), (2) VO(2) at ventilatory threshold (VT), (3) distance on the 6-minute walk, and (4) peak VO(2).
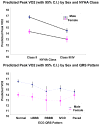
Results: The women were younger than the men and more likely to have a nonischemic etiology and a higher ejection fraction. Dose of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor (ACEI) was lower in the women, on average. The lower ACEI dose may reflect the higher use of angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB) in women. Both the peak VO(2) and the 6-minute walk distance were significantly lower in the women than in the men. Perhaps the most significant finding in this dataset of baseline characteristics is that the peak VO(2) for women was significantly lower than that for men with similar ventricular function and health status.
Conclusion: Therefore, in a well-medicated, stable, class II-IV HF cohort of patients who are able to exercise, women have statistically significantly lower peak VO(2) and 6-minute walk distance than men with similar health status and ventricular function. These data should prompt careful thought when considering prognostic markers for women and listing for cardiac transplant.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00047437.
Figures




References
-
- American Heart Association. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics - 2006 Update. Dallas, Texas: American Heart Association; 2006. ©2006, American Heart Association. 2006. Ref Type: Generic.
-
- Koelling TM, Chen RS, Lubwama RN, L’Italien GJ, Eagle KA. The expanding national burden of heart failure in the United States: the influence of heart failure in women. Am Heart J. 2004;147:74–78. - PubMed
-
- Kimmelstiel CD, Konstam MA. Heart failure in women. Cardiology. 1995;86:304–9. - PubMed
-
- O’Meara E, Clayton T, McEntegart MB, McMurray JJ, Pina IL, Granger CB, et al. Sex differences in clinical characteristics and prognosis in a broad spectrum of patients with heart failure: results of the Candesartan in Heart failure: Assessment of Reduction in Mortality and morbidity (CHARM) program. Circulation. 2007;115:3111–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- U01 HL064257/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 5U01HL066461/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 5U01HL064264/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL064250/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P60AG10484/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG018915/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL064265/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL066497/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL064264/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 5U01HL066482/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 5U01HL066497/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL068980/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 5U01HL064250/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 5U01HL064265/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL066491/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 5U01HL068973/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 5U01HL064257/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL066482/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 5U01HL063747/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 5U01HL066491/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R37AG18915/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AG018915/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL066494/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 5U01HL066501/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL066461/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL068973/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 5U01HL068980/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL063747/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 5U01HL066494/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL066501/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

